- 2021-04-14 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 8页

申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
小学六年级英语总复习资料
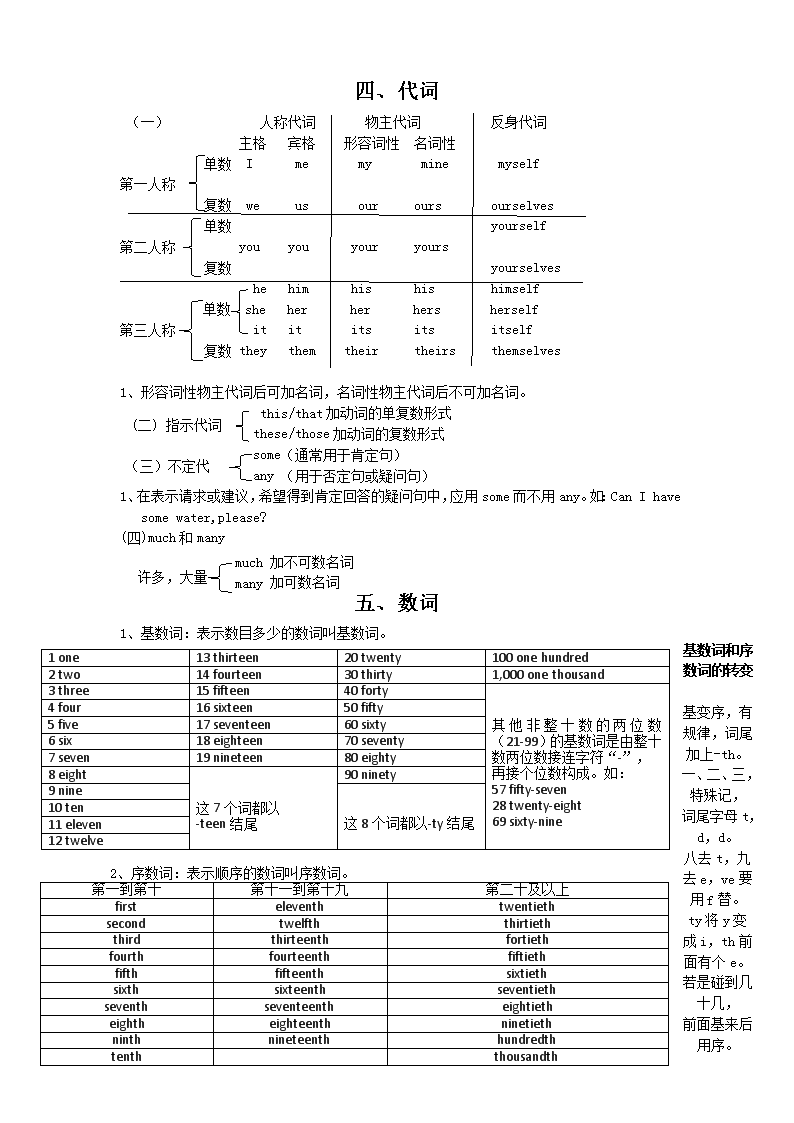
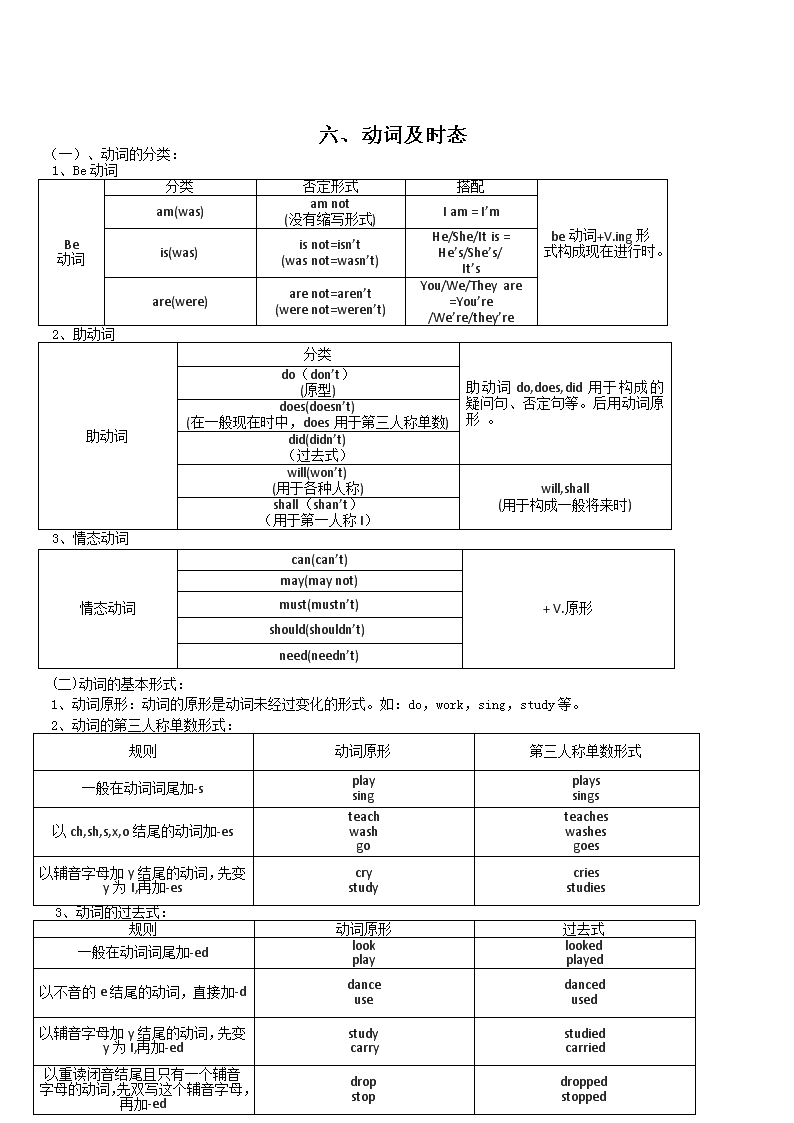
1、 元音字母:Aa Ee Ii Oo Uu 2、 大写字母的应用: ①句子第一个单词的首字母要大写。 ②人名、国家名、地名、语言等专有名词 首字母要大写。 ③星期、月份、节目的单词首字母要大写。 ④表示“我”的字母“I”永远要大写。 ⑤文章标题除冠词、介词、或连词外,每个单词的首字母一般要大写。 一、字母 不定冠词:a、 an 定冠词 :the 2、a、an的使用取决于其后名词以什么音开头,而不是以什么字母开头 。一般情况下,以元音字母开头的单词前要用不定冠词an。 注意:an hour 一小时 an honest boy 一个诚实的男孩 a university student 一个大学生 a usual way 一个通常的方法 3、特指独一无二的事物,前面一般加定冠词the。 Eg:The Great Wall is in China.长城在中国。 4、the用于乐器名称之前。 Eg:play the piano 弹钢琴 play the guitar 弹吉他 1、冠词 二、冠词 三、名词 可数名词 :表示可以用数目来计算的人、事物和概念的普通名词。(有单复数形式) 1、名词 不可数名词:表示无法用数目来计算的事物和概念的普通名词。(只有单数形式) 2、可数名词的复数变化规则: ①一般情况下直接加-s。(浊辅音和元音后读/z/,清辅音后读/s/) pen(pens)、 t eacher(teachers) ②以s sh x ch结尾的词,一般情况下加-es。 bus(buses)、 box(boxes)、dish(dishes)、peach(peaches) ③以“辅音字母+y”结尾的名词先改y为i,再加-es,es读/z/ family(families)、cherry(cherries)、factory(factories)、candy(candies) 但boy除外boy(boys) ④以f或fe结尾的词,多数变f或fe为v再加-es。 knife(kives)、leaf(leaves)、wolf(wolves) ⑤以o结尾的词后加-es或-s。(表示有生命的加es,没有生命的加s) tomato(tomatoes)、potato(potatoes)、hero(heroes)、photo(photos) ⑥改变中间元音。 man(men)、woman(women)、foot(feet)、tooth(teeth)、mouse(mice) ⑦词尾加en或ren。 Ox(oxen)、child(children) ⑧单复数同行。 fish(fish)、sheep(sheep)、deer(deer) 四、代词 (一) 人称代词 物主代词 反身代词 主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性 单数 I me my mine myself 第一人称 复数 we us our ours ourselves 单数 yourself 第二人称 you you your yours 复数 yourselves he him his his himself 单数 she her her hers herself 第三人称 it it its its itself 复数 they them their theirs themselves 1、形容词性物主代词后可加名词,名词性物主代词后不可加名词。 (二) 指示代词 this/that加动词的单复数形式 these/those加动词的复数形式 (三)不定代词 some(通常用于肯定句) any (用于否定句或疑问句) 1、在表示请求或建议,希望得到肯定回答的疑问句中,应用some而不用any。如:Can I have some water,please? much 加不可数名词 many 加可数名词 (四)much和many 许多,大量 五、数词 基数词和序数词的转变 基变序,有规律,词尾加上-th。 一、二、三,特殊记, 词尾字母t,d,d。 八去t,九去e,ve要用f替。 ty将y变成i,th前面有个e。 若是碰到几十几, 前面基来后用序。 1、基数词:表示数目多少的数词叫基数词。 1 one 13 thirteen 20 twenty 100 one hundred 2 two 14 fourteen 30 thirty 1,000 one thousand 3 three 15 fifteen 40 forty 其他非整十数的两位数(21-99)的基数词是由整十数两位数接连字符“-”, 再接个位数构成。如: 57 fifty-seven 28 twenty-eight 69 sixty-nine 4 four 16 sixteen 50 fifty 5 five 17 seventeen 60 sixty 6 six 18 eighteen 70 seventy 7 seven 19 nineteen 80 eighty 8 eight 这7个词都以 -teen结尾 90 ninety 9 nine 这8个词都以-ty结尾 10 ten 11 eleven 12 twelve 2、序数词:表示顺序的数词叫序数词。 第一到第十 第十一到第十九 第二十及以上 first eleventh twentieth second twelfth thirtieth third thirteenth fortieth fourth fourteenth fiftieth fifth fifteenth sixtieth sixth sixteenth seventieth seventh seventeenth eightieth eighth eighteenth ninetieth ninth nineteenth hundredth tenth thousandth 六、 动词及时态 (一) 、动词的分类: 1、Be动词 Be 动词 分类 否定形式 搭配 be动词+V.ing形式构成现在进行时。 am(was) am not (没有缩写形式) I am = I’m is(was) is not=isn’t (was not=wasn’t) He/She/It is = He’s/She’s/ It’s are(were) are not=aren’t (were not=weren’t) You/We/They are =You’re /We’re/they’re 2、助动词 助动词 分类 助动词do,does,did用于构成的疑问句、否定句等。后用动词原形 。 do(don’t) (原型) does(doesn’t) (在一般现在时中,does用于第三人称单数) did(didn’t) (过去式) will(won’t) (用于各种人称) will,shall (用于构成一般将来时) shall(shan’t) (用于第一人称I) 3、情态动词 情态动词 can(can’t) + V.原形 may(may not) must(mustn’t) should(shouldn’t) need(needn’t) (二)动词的基本形式: 1、动词原形:动词的原形是动词未经过变化的形式。如:do,work,sing,study等。 规则 动词原形 第三人称单数形式 一般在动词词尾加-s play sing plays sings 以ch,sh,s,x,o结尾的动词加-es teach wash go teaches washes goes 以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先变y为I,再加-es cry study cries studies 3、动词的过去式: 规则 动词原形 过去式 一般在动词词尾加-ed look play looked played 以不音的e结尾的动词,直接加-d dance use danced used 以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先变y为I,再加-ed study carry studied carried 以重读闭音结尾且只有一个辅音字母的动词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed drop stop dropped stopped 2、动词的第三人称单数形式: 4、 动词的现在分词(也就是动词的-ing形式): 规则 动词原形 现在分词 一般在动词后直接加-ing go work going working 以不发音的e结尾的动词,去e加-ing come make coming making 以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音音字母的动词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing swim shop swimming shopping 少数几个以ie结尾的动词,先变ie为y,再加-ing die lie dying lying (三)动词的时态: 1、一般现在时 ⑴一般现在时的形式:一般现在时时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词应用第三人称单数形式。 ⑵、一般现在时的基本用法: ①表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与频率副词连用。常见的频率副词有:always、usually、often、sometimes、never等。如: My mother often gets up at 6 o’clock. 我妈妈经常在六点半起床。 ②表示客观存在的真理或科学事实。如: The earth moves around the sun. 地球围绕太阳转。 ③表示现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。如:I am a student. 我是一名学生。 分类 形式 例句 be动词 的一般现在时 第一人称单数+am I am a student. 第三人称单数+is He/She is a worker. It is sunny today. 第二人称单数/各人称复数+are You are a beautiful girl. We/They are good friend. 实义动词 的一般现在时 第三人称单数+动词第三人称单数形式 He/She goes to school by bus. It works well. 第一、二人称单数/各人称复数+动词原形 I/You study hard. We/You/They go to school every day. 2、一般过去时 ⑴一般过去时的形式:一般过去时是由be动词或实义动词的过去式构成的。 ⑵实义动词的一般过去时的否定式和疑问式都应用助动词do的过去式did帮助完成。如: ①Did you watch TV last night? ②I didn’t do to school this morning. ⑶一般过去时的基本用法: ①有确定的过去时间状语时要用一般过去时。 如:I visited my uncle yesterday.昨天我拜访了我的叔叔。 ②表示过去一段时间内的经常性、习惯性或反复性的动作要用一般过去时。 如:She often played computer games in 2013.2013年她经常玩电脑游戏。 ③表示主语过去的特征或性格要用一般过去时。 如:She was a teacher.她过去是一名教师。 分类 形式 例句 be动词的一般过去时 第一人称单数/第三人称单数+was I was tired yesterday. He/She was a teacher last year. It was a good day yesterday. 第二人称单数+were 各人称复数+were You were short last year. We/You/They were happy last night. 实义动词的一般过去时 各人称单/复数+动词的过去式 I/He/She/You got up at six this morning. We/You/They had a good time last week. 3、一般将来时 ⑴一般将来时的形式: ①“be going to+V.原形” 主语 be动词的变化 其他 I am going to water flowers You are going to He/She/It is going to 第三人称单数 is going to 所有表示复数的主语 are going to be going to中的be根据主语的不同而选择使用: ②“will/shall+V.原形”表示将来时时,shall仅与第一人称搭配使用,will与各种人称使用。 如:I/ We shall go shopping tomorrow.我/我们打算明天去购物。 He/She/They will come next week.他/她/他们下周来。 ⑵一般将来时的基本用法: ①一般将来表示将要发生的动作或状态。如:I will/shall go tomorrow.我明天去。 3、现在进行时 ⑴现在进行时的形式:现在进行时由“be动词+V.ing形式”。 形式 例句 第一人称单数+am+V.ing形式 I am doing my homework now. 第三人称单数+is+ V.ing形式 He/She is watching TV. The kite is flying in the sky. 第二人称单数/各人称复数+are+ V.ing形式 We/You/They are singing. ⑵现在进行时的基本用法: ①表示此时此刻正在进行的动作。如: -What are you doing? 你在做什么? -I am reading English. 我在读英语。 ②当时间状语为now或句子中有look,listen等词时,表示动作正在进行,这时要用现在进行时,如: -They are playing football now. 现在他们在踢球。 -Listen!She is singing an English song.听,她正在唱英语歌 。 七、介词 (一)介词的常见用法: 1、at、in、on在表示时间时的区别: ⑴ at:①表示具体的时间点,如:at five o’clock ⑵ in:①常与上午、下午、晚上等词连用,如:in the morning,in the afternoon,in the evening等。 ⑶ on:①常与星期连用,如: on Monday,on Sunday等。 ②表示具体的某一天,如:onJune 1 st ,on May 3 rd等。 ③表示在某天的上午、下午或晚上,如:on Saturday morning等。 ②常与月份、季节、年份、连用,如:in July ,in spring,in 2017等。 2、in和at在表示地点时的区别: ⑴ in+大地点,如:He lives in Shanghai. ⑵ at+小地点,如:at the door,at the corner of the street 3、by,with和in表示方式时的区别 ⑴by:表示“以...”方法、手段或泛指某种交通工具。如: I go to school by bike every day. ⑵with:表示“用;以”,一般接具体的交通工具和手段。如:She cut the cake with a knife. ⑶in:表示“用某种语言”;穿着,戴着。如:The girl in a red T-shirt is my sister. 4、in、on、under、用于方位时的区别: ⑴in 在...里面 如:in the box 在盒子里面 ⑵on 在...上面 如:on the desk在桌子上面 ⑶under 在...下面 如:under the chair 在椅子下面 八、句型 (一)、陈述句: 1、陈述句的肯定式: (1)主语+系动词+表语. 如:-This is my father.这是我的爸爸.-It’s warm today.今天暖和。 (2)主语+谓语动词. 如:-The teacher smiled.老师笑了。 (3)主语+谓语动词+宾语. 如:-I want some chicken.我想要一些鸡肉。 2、陈述句的否定式: (1)主语+be动词+not+其他. 如:-Those are not my glasses.那不是我的眼镜。 (2)主语+助动词(do/does/did)+not+实义动词+其他 如:-I don’t like grapes.我不喜欢葡萄。 (3)主语+情态动词+not+实义动词+其他. 如:-I can’t find Tony.我找不到Tony. 3、否定式的缩写形式: is not=isn’t are not=aren’t do not=don’t does not=doesn’t did not=didn’t will not=won’t were not=weren’t was not=wasn’t (二)疑问句: 1、一般疑问句: (1)be+主语+表语? 如:-Are you a student? 你是一名小学生吗? (2)情态动词(或助动词)+主语+谓语动词+其他? 如:-Can you swim? 你会游泳吗? - Do you like English? 你喜欢英语吗? 2、特殊疑问句 :特殊疑问句是对句子中某一部分提问的疑问句。通常以What, Who, Whose, Which, When, Why, Where, How等词引导。 (三)祈使句: 1、祈使句的肯定式: 谓语动词用原形。如:-Look at the blackboard.请看黑板。 2、祈使句的否定式 : (1)Don’t+动词原形. 如:-Don’t worry.别担心。 -Never do that again! 再也不要那样做了。 3、祈使句的let式: (1)Let’s+动词的原形. 如:-Let’s go home.让我们回家吧! 4、祈使句的请求式:如:-Turn on the radio, please.请把收音机打开。 5、祈使句的命令式:如:-Stop talking! 别讲话! 6、祈使句的禁止式:如:-No swimming. 禁止游泳。 7、祈使句的提醒式:如:-Look out! The car is coming.当心!车来了。 (四)感叹句: 1、由what引导的感叹句: (1)What+a/an+形容词+可数名词单数+(主语+谓语)! 如:-What a beautiful desert (it is)! 多么美丽的沙漠啊! 2、 由How引导的感叹句:; (1) How +形容词+主语+谓语! 如:-How beautiful the flower is! 多么漂亮的花啊 (五) There be结构: 1、There be 结构的肯定式: (1)There is +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点/时间状语. 如:-There is a book on the desk. 桌子上有一本书。 (2) There are+可数名词复数+地点/时间状语. 如:-There are some flowers in there grade.花园里有一些花。 2、There be结构的否定式是在谓语动词后加“not”或“no”,表示“没有”之意。如果句中有some,变否定式时需将some变为any。 3、There be结构的疑问式: (1)There be结构变成一般疑问句时,要把be动词提前至there前。 其肯定回答用“Yes ,there is/are”.否定回答用“No, there isn’t /aren’t”. 如:-Is there a computer in your room?你房间有电脑吗? -Yes,there is./ No, there isn’t.是的,有。/不,没有。 4、There be 的就进原则: 如:-There is a boy and two girls in the classroom.教室里有一个男孩和两个女孩。 -There are three pens and a pencil in the desk. 桌子上有三只钢笔和一只铅笔。 5、There be 和have 的区别: There be (某地有某人或某物,强调某处有) Have (某人或某物拥有,强调某人有)查看更多