- 2021-04-20 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 111页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
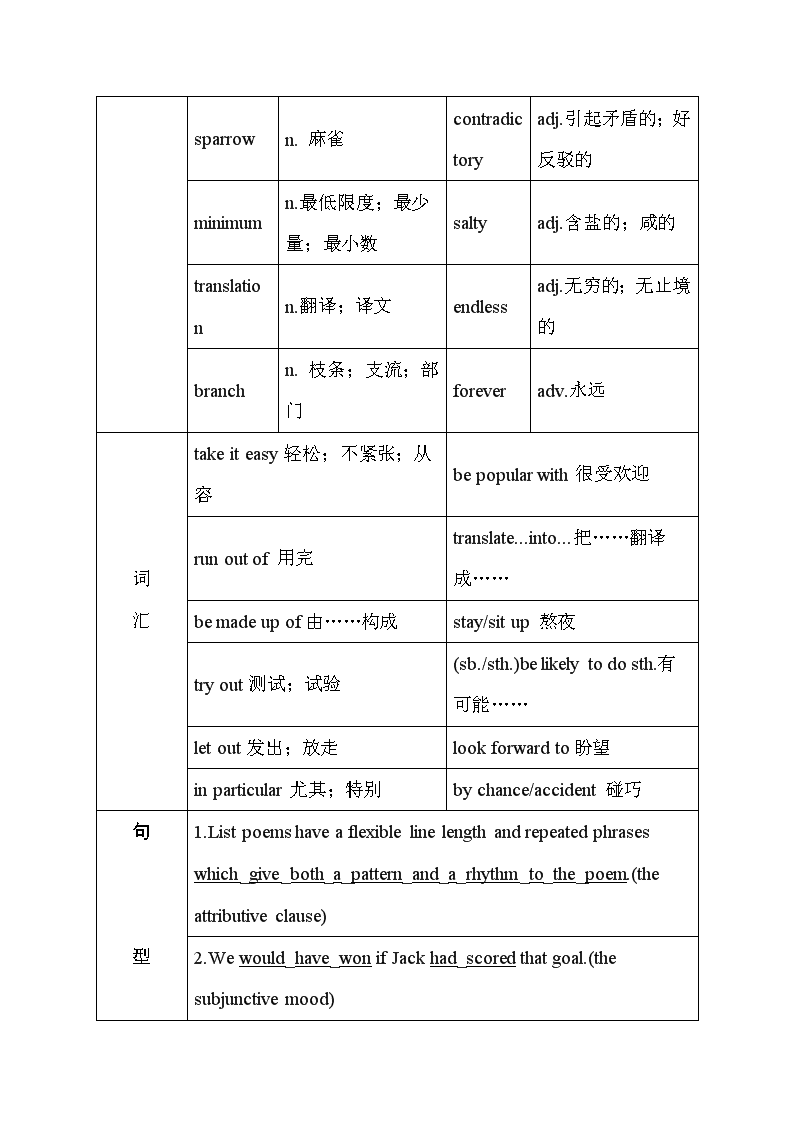
2020届一轮复习人教版选修六Unit2Poems单元教案(51页word版)
2020届一轮复习人教版选修六Unit 2Poems单元教案 本单元的中心话题是诗歌。阅读文章中涉及诗歌的韵律和节奏,并介绍了几种不同内容和形式的简单诗歌。本单元语言知识的选择和听说读写等语言技能的训练主要围绕“诗歌”这一主题进行。本单元的目的在于帮助学生掌握与“诗歌”这一主题有关的词汇知识,让学生了解诗歌的一些基本特征和写作方法,从而学会欣赏这些优美的文学作品,最终能够自己尝试写简单的诗歌。 本单元的主要教学内容如下表所示: 类别 课程标准要求掌握的内容 话题 Different types of poems;reading,writing and listening to poetry transform[来源:学§科§网] v.转化;转换;改造;变换 sorrow n.悲伤;懊悔;悲痛[来源:Z#xx#k.Com] [来源:学|科|网] 词[来源:学科网ZXXK] 汇 exchange n.& v.交换;交流;调换 librarian n.图书馆长;图书管理员 sponsor v.& n. 发起(人);主办(者);倡议(者) section n.部分;切下的块;节 concrete adj.具体的 diploma n.毕业文凭;学位证书 flexible adj. 灵活的;可弯曲的 blank n.& adj.空白;空白的;茫然的 appropriate adj.适当的;正当的 compass n.指南针;罗盘 eventually adv. 最后;终于 bride n.新娘 tick v.给……标记号 bridegroom n.新郎 convey v.传达;运送 championship n. 冠军称号 tease v.取笑;招惹;戏弄 darkness n.黑暗;漆黑 rhyme n.& v.韵;(使)押韵 warmth n.暖和;温暖 nursery n. 托儿所 scholarship n.奖学金;学问;学术成就 diamond n.钻石;菱形 pianist n. 钢琴家;钢琴演奏者 pattern n.模式;式样;图案 violinist n.小提琴演奏者 cottage n. 村舍;小屋 load n. 负担;负荷物 sparrow n. 麻雀 contradictory adj.引起矛盾的;好反驳的 minimum n.最低限度;最少量;最小数 salty adj.含盐的;咸的 translation n.翻译;译文 endless adj.无穷的;无止境的 branch n. 枝条;支流;部门 forever adv.永远 词 汇 take it easy轻松;不紧张;从容 be popular with很受欢迎 run out of 用完 translate...into...把……翻译成…… be made up of由……构成 stay/sit up 熬夜 try out测试;试验 (sb./sth.)be likely to do sth.有可能…… let out发出;放走 look forward to盼望 in particular尤其;特别 by chance/accident 碰巧 句 型 1.List poems have a flexible line length and repeated phrases which_give_both_a_pattern_and_a_rhythm_to_the_poem.(the attributive clause) 2.We would_have_won if Jack had_scored that goal.(the subjunctive mood) 3.Another simple form of poem that students can easily write is the cinquain,a poem made_up_of_five_lines.(past participle as the attributive) 4.When I was a baby,my mother used_to read me nursery rhymes.(used to do sth.) 5.With_so_many_different_forms_of_poetry_to_choose_from,students may eventually want to write poems of their own.(with+object+objective complement) 功 能 语 法 虚拟语气(Subjunctive Mood)(2) If Rob hadn't injured himself,we would have won. If she had studied harder,she would have got the diploma. 教 学 重 点 1.Get students to know about different types of poems,some poetic devices like rhythm,rhyme,repetition,sound patterns and imagery. 2.Have students learn some useful new words and expressions about poetry and let them learn effective ways to master them. 3.Enable students to grasp and use the expressions of intention and plans. 4.Let students learn the new grammar item:the subjunctive mood(2). 5.Develop students' listening,speaking,reading and writing ability. 教学 难点 1.Enable students to master the use of the subjunctive mood. 2.Let students learn to create their own poems. 3.Develop students' integrative skills. 课 时 安 排 Periods needed:6 Period 1 Warming Up,Pre-reading,Reading and Comprehending Period 2 Language Study Period 3 Grammar—the Subjunctive Mood(2) Period 4 Listening and Speaking Period 5 Reading and Writing Period 6 Summing Up,Learning Tip and Assessment Period 1 Warming Up,Pre-reading, Reading and Comprehending 教学内容分析 This is the first teaching period of this unit.The central part of this period is the reading passage with the name of A Few Simple Forms of English Poems showing the students a few kinds of simple English poems. Warming Up gives three questions for students to discuss so that they can recall any poems they have ever learned and think about different reasons why people write poems. Pre-reading provides one question for students to think about and a table for students to fill in so as to help students focus on the topic of the reading passage and lead the students to skim the poems on the following pages and know about the general idea of the text. Reading mainly explains the reasons why people write poetry and introduces five simple forms of English poems.Nursery rhymes are the first poems that children will hear.These poems may not make any sense but they are easy to learn and recite.It is a good way for children to learn about language.List poems often list things,usually having many lines.They have repetition in them and sometimes they have words that rhyme.Cinquains are all made up of five lines and have the fixed structure.Haiku is a Japanese form of poetry that is made up of 17 syllables.It is almost like a photo or painting as it creates a strong image using very few words.Tang poems are famous poems from Ancient China.They have strong imagery and are often about the bringing together of opposites. Comprehending consists of three groups of exercises for the students to do so as to help the students to get a better understanding of the text,that is to say,to help the teacher to check how much the students have understood the text. 三维目标设计 Knowledge and skills 1.To know the meanings of the following new words and phrases: tick(给……标记号),rhyme(韵;押韵),convey(传达;运送),nursery(托儿所),concrete(具体的),contradictory(引起矛盾的;好反驳的),diamond(钻石;菱形),flexible(灵活的;可弯曲的),pattern(模式;式样;图案),cottage(村舍;小屋),sparrow(麻雀),take it easy(轻松;不紧张;从容),run out of(用完),be made up of(由……构成),tease(取笑;招惹;戏弄),salty(含盐的;咸的),endless(无穷的;无止境的),minimum(最低限度;最少量),translation(翻译;译文),branch(枝条;支流;部门),in particular(尤其;特别) 2.To learn about some simple forms of English poems. 3.To develop the students' reading ability by skimming and scanning the passage. 4.To develop the students' speaking ability by talking about some features of some simple forms of English poems. Process and methods 1.While doing Warming Up the teacher can ask the students to think back and try to remember poems from both their early childhood and more recent years.Ask students to complete Exercise 1 in groups.Ask them what they notice about these poems,then get students to recite any poems or parts of poems they can remember so as to arouse their interest in studying the whole unit. 2.During Pre-reading the teacher can go around the classroom and discuss the questions with several students.This discussion should be student-centered and arouse students' interest in English poetry.The teacher should also ask the students to skim the text so as to let them have a general knowledge of some simple forms of English poems. 3.While doing Reading and Comprehending,the teacher may first have the students close their books and listen to the text with their eyes closed.This gives the students the opportunity to listen to the sounds or “music” of the poems before reading them in more detail.Then ask the students to read the text quickly to get the general idea of the passage.After detailed reading of the passage,students are encouraged to answer some questions and discuss the features of each kind of the poems. 4.To consolidate the contents of the reading passage,the students should be required to retell the five kinds of poems in their own words at the end of the class. Emotion,attitude and value 1.To cultivate students' appreciation of poetry and the ability of understanding,enjoying and writing poems. 2.To develop students' sense of cooperative learning. 教学重、难点 1.To enable the students to learn about some simple forms of English poetry and to develop their reading ability. 2.To enable the students to write their own poems. Step 1 Warming up 1.Vocabulary in Reading Match the words and phrases with their proper meanings. 1.convey ( )A.sameness of sound between words or syllables,esp.in the end of lines 2.cottage ( )B.a strong feeling such as love,fear or anger 3.tease ( )C.make fun of somebody in an unkind way 4.rhyme ( )D.a place where young children are cared for 5.translate ( )E.make(ideas,feelings,etc.)known to another person 6.endless ( )F.use up 7.nursery ( )G.small simple house,esp.in the country 8.emotion ( )H.relax 9.take it easy ( )I.express sth.in a different language 10.run out of ( )J.without end Suggested answers:1.E 2.G 3.C 4.A 5.I 6.J 7.D 8.B 9.H 10.F 2.Warming up by asking students to complete Exercise 1 in groups.Get the students to recite the little poems and songs they can remember.Ask them what they notice about these poems.For example,perhaps they have a strong beat,or they rhyme,or they play with words and sounds,or perhaps some of them are funny because they make no sense. 3.Warming up by doing Exercise 2 with students.Then get them into groups as this might prompt their memories.Get the students to recite any poems or parts of poems they can remember.(If the students can't recite any poems or parts of poems,prepare a couple of poems that they would know,in Chinese or English.) 4.Tell students that there are many reasons why people write poetry.Give the examples in Exercise 3.Ask students the reasons they think the poets wrote the poems they have just recited.Write their suggestions on the blackboard. Step 2 Pre-reading 1.Match the following information. Du Fu Tang Dynasty Fan Zhongyan Song Dynasty Meng Haoran Modern Guo Moruo Modern Xu Zhimo Tang Dynasty Byron America Shelly England Whitman England Tagore India Suggested answers:Du Fu:Tang Dynasty;Fan Zhongyan:Song Dynasty;Meng Haoran:Tang Dynasty;Guo Moruo:Modern;Xu Zhimo:Modern;Byron:England;Shelly:England;Whitman:America;Tagore:India 2.Ask students to do Exercise 1 in groups.Get them to tell the class their favourite poems and the reasons.This might be something they find hard to articulate as the poem might just give them a special feeling that's hard to talk about.Or they might say things like:It makes me feel sad.I like the sounds in it.I like its language,it's funny,and my mother used to recite it to me... 3.The purpose of Exercise 2 is to practice an important reading skill:scanning a text,that is,looking through a text quickly to find specific information. Suggested answers: Which poem A B C D E F G H describes a person? √ tells a story? √ describes an aspect of a season? √ √ √ is about sport? √ is about things that don't make sense? √ is recited to a baby? √ describes a river scene? √ has rhyming words at the end of lines? √ √ repeats words or phrases? √ √ √ Step 3 Reading and comprehending 1.Fast-reading:Read the reading passage quickly,try to get its general idea and answer the following questions. (1)What is the main idea of the reading passage? ________________________________________________________________________ (2)How many kinds of poems does the reading passage talk about? And which of the following is not mentioned? A.Nursery rhymes. B.Tang poems. C.Haiku. D.Adverb poems. E.List poems. F.Cinquain. Suggested answers: (1)A brief introduction of a few simple forms of English poems. (2)Five.D is not mentioned. 2.Detailed-reading:Read the text thoroughly and do the following exercises.(You may do some searching reading when necessary.) (1)Give out the names of the forms of poems according to the descriptions. ①______ are the first poems that children will hear.They are often sung.Children love to move and dance to them because they have strong regular rhythms.They enjoy the rhymes and the way they play with sounds. ②______ is made up of five lines and has the following structure: Line 1:a noun that names the subject of the poem Line 2:two adjectives that describe the subject Line 3:three verbs ending with-ing that describe the subject's actions Line 4:four words that give the writer's opinions or feelings about the subject Line 5:a word that gives another name for the subject ③______ is a centuries-old form of Japanese poetry.It is made up of 17 syllables and has the following structure: Line 1:5 syllables Line 2:7 syllables Line 3:5 syllables ④______ are a list of things.They can have as many lines as the writer likes.Sometimes they have repetition in them and sometimes they have words that rhyme.When a list poem has rhyming words,it also has a regular rhythm. ⑤When translated into English,______ have a free form(that is,without a regular rhythm)and do not rhyme.They have strong imagery and are often about the bringing together of opposites. (2)Find the strong rhythm and rhyme in Poem A. e.g.In the first two lines,there are word_&_mockingbird. So in the following lines,there are ______;______;______;______. (3)What's the difference between Poems B and C though they are both list poems? ________________________________________________________________________ (4)Which of the poems in the reading passage can give you a clear picture in your mind? ________________________________________________________________________ (5)Can you find out the 17 syllables in Poem F? e.g.“A” has 1 syllable,“fallen” has 2 syllables,while “blossom” has 2 syllables. ________________________________________________________________________. (6)Can you give a proper title to Poem H either in English or Chinese? ________________________________________________________________________ Suggested answers: (1)①Nursery rhymes ②The cinquain ③Haiku ④List poems ⑤Tang poems (2)sing & ring;brass & looking-glass;broke & billy-goat;away & today (3)Poem B repeats phrases and rhymes,while Poem C does not. (4)Most probably Poems D,F,G and H. (5)A(1);fallen(2);blossom(2);Is(1);coming(2);back(1);to(1);the(1);branch(1);Look(1);a(1);butterfly(3) (6)望夫石/A Loyal Wife Step 4 Language study Deal with language problems if any(words or sentences students might not understand)to help the students to have a better understanding of the text. Step 5 Listening,reading aloud and underlining Ask students to read the passage aloud to the tape and let them pay attention to the pronunciation of each word and the pauses within each sentence.Tell them to pick out all the useful expressions or collocations from the passage while reading and copy them to the notebook after class as homework. Collocations:make sense,give...a strong impression,on fire,take it easy,run out of,make up of,be translated into,day by day,in particular. Step 6 Structure analyzing After reading,ask students to discuss the text structure. Keys for reference: This passage is an introduction of some of the simple forms of English poems.The first paragraph introduces the topic and the theme of the text,explaining the purpose of poetry writing,that is,to give readers a strong impression or to convey certain emotions.From the second paragraph,the text analyses the different kinds of poems and gives examples for reference.The last paragraph encourages students to have a try and write poems of their own. Step 7 Retelling Ask students to talk about the different kinds of poems in their own words.Give them some key words and expressions on the blackboard.Then let them try to retell the passage. Step 8 Homework 1.Learn the useful new words and expressions in this period by heart. 2.Try to find some selections of poems and appreciate their beauty and eventually try to write some poems of your own. Step 9 Reflection after teaching ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Reading:A Few Simple Forms of English Poems 李东玲,海南省儋州市民族中学,本教案获2008年度“教科杯” 海南省中小学教师教学论文和教学设计大赛二等奖 教学 课题 Unit 2 Poems A Few Simple Forms Of English Poems(Reading) 教学 设计 理论 依据 《基础教育课程改革纲要(试行)》对于课程实施和教学过程有明确的要求:倡导学生主动参与、乐于探究、勤于动手,培养学生搜集和处理信息的能力、获取新知识的能力、分析和解决问题的能力以及交流与合作的能力。教师在教学过程中应与学生积极互动、共同发展,要处理好传授知识与培养能力的关系,注重培养学生的独立性和自主性,引导学生质疑、调查、探究,在实践中学习,促进学生在教师指导下主动地、富有个性地学习。 教材 分析 本课是新课标高中英语选修6第二单元中的阅读课,是一篇介绍诗歌基础知识的文章。文章从诗歌创作的动机、种类、特点及读者对象等方面简要介绍了五种不同风格、不同特色的诗歌。旨在通过本单元的学习,使学生在初步了解和掌握诗歌这一文学形式的基础常识的基础上,进行简单的诗歌创作。 学情 分析 本节课的教学对象是高二学生,他们很了解中文诗歌的种类、风格、特色,对英文诗歌的学习充满了浓厚的兴趣,想知道:中英文诗歌是否一样?同时他们也有着丰富的想象力和活跃的思维,具有一定的分析和解决问题的能力,已掌握相关的认知策略,如分析、想象、推理、归类、总结、记忆等。大部分学生的基础知识仍然较为薄弱,运用英语进行交际活动的能力较差,但他们好胜心强,渴望在班集体里得到他人的承认。个别学生基础较好,能主动配合老师,具有独立、爱表现的特点。因此,只有设计使他们感兴趣的活动,因材施教,才能让全班同学投入到课堂活动中来。 教 学 三维目标: 1.知识目标 目 标 Make the students master the following words,phrases and sentence patterns. ★Important words: poem,poetry,recite,aspect,convey,rhyme,rhythm,nursery,diamond,cottage,balloon,sparrow,tease,salty,endless,branch,translation,transform ★Important phrases: take it easy,run out of,make up of ★Important sentence patterns: ...they delight small children because... We would have won...if Jack had scored that goal. 2.能力目标 ★To learn the main developing steps of the history of English poetry. ★To learn the characteristics of different forms of poems. ★To improve students' reading ability. ★To practice writing simple poems. 教 学 目 3.情感态度目标 标 利用多媒体手段营造积极、和谐的教学气氛,使学生不自觉地进入情景之中,充分调动学生的思维活动和情感体验,引起学生的共鸣。本部分旨在培养学生通过阅读手段,获取有关英国诗歌方面的知识,提高他们的素质,扩大他们的国际视野,提高阅读能力,强化文化意识,激发他们热爱我国瑰丽的诗歌文化宝库的爱国热情。 教学重点: ★Master the important new words,phrases and sentence patterns. ★Collect the reasons why the poets write poems. ★The similarities and differences between the Chinese and English poets and poems. 教学难点: ★Find out the characteristics of each kind of poems. ★Practice writing simple poems. 教 学 策 略 ★培养学生搜集与处理信息的能力(“有意义接受学习”教学法) ★培养学生获取新知识的能力(探究式教学法) ★培养学生分析和解决问题的能力(问题式学习教学法、任务型教学法) ★培养学生交流与合作的能力(合作学习教学法) 教 学 ★ 用 具 多媒体辅助:将本课所需要的动画、录音、图片、文字、图表和音乐制成CAI软件使抽象的语言变得直观,为学生运用英语进行交际创设情景。 ★黑板:展示本课的重点单词、短语、句型。 教学过程设计 教学步骤 活动内容 设计意图 Task 1 Warming Up (4 minutes) ★Talk about poets and poems the students learned before. ★Let some students list the reasons why people write poems on the blackboard. 运用“有意义接受学习”教学法: 提示学生先回忆原有知识,获得成就感,增强自信心,并总结出写诗意图,激发学生积极思考,领悟本课教学目标。为学习英文诗歌作好铺垫,阐明新旧知识的各种关系,促进新知识的理解。 Task 2 Presentation (5 minutes) ★Listen to the tape about the reading passage. ★After listening,tick the correct box(es) of each question in the form in Pre-reading. 运用探究式教学法: 该任务鼓励学生主动参与、主动探究、主动思考,概括出每首诗歌的主题大意。 Task 3 Practice (15 minutes) ★According to the Chinese meaning,fill in the correct form of the word. e.g.The music is written in a ______(节奏)of three beats to a bar. ★Ask the students to answer the questions in Exercise 2 and Exercise 3 in Comprehending according to the text. ★Find out the information to complete the following form. Forms of poems Characteristics 运用问题式学习教学法、任务型教学法: 学生带着问题再一次详细阅读并理解全文,解决问题,完成任务,做好语言输入储备工作。该任务提高了学生的探究能力,充分发挥学生的自主性。此过程中,还能体现师生、生生之间互相交流、互相探讨的合作学习精神。 Task 4 Group Work(15 minutes) ★Hold an English poem writing competition: Four students work as a group.Practice writing simple poems.Then show their poems to others. 运用合作学习教学法: 以竞赛为前提,唤起学生的好胜激情。小组成员各抒己见,培养学生交流与合作能力。把学生所学知识发散、扩展、升华并输出,学以致用,学生又获得成就感。 Homework(1 minute) ★Practice writing more poems. ★Ask the students to collect at least five English poems with different forms. You can search the Internet if you want to know more about English poems. 运用任务型教学法: 课外作业,课堂小组活动延伸到课外,学生仍然可以互相合作完成该写作任务。该环节是本课所有教学环节的延续。 Ⅰ.Famous poetry in English Reading poetry brings people from different places and different times together.More than any other form of literature,poetry plays with sounds,words and grammar.That makes poetry difficult to write,but very interesting to read.Poetry also calls up all the colors,feelings,experiences and curious images of a dream world. Though it has a short history,there is a lot of good English poetry around.The seventeenth century was a great time for English poetry.Shakespeare is most famous for his plays.His sonnets,however,belong to the best English poetry.In the next generation of the English poets we meet John Donne.Chinese readers admire his works because of his use of surprising images that reminds them of the works of poets such as Su Dongpo. Before the end of the century,there was another famous writer,John Milton.Once published,his works became famous for the absence rhyme at the end of each line.In the eighteenth century it was Alexander Pope who wrote the finest poetry in England. The next period that produced a great number of fine poets was the nineteenth century.Greatly loved in China are the English Romantic poets.John Keats died at a very young age in 1821,while William Wordsworth,who spent much of his time in his English Lake District,lived to the age of the 80 and died in 1850.The nature poems by William Wordsworth,George Gordon Byron's Isles of Greece and the sonnets and long poems by John Keats have long been favorites.The style in their poems has often led to comparisons with poets such as Du Fu and Li Bai. Finally,modern poets have their special attraction because they stand closest to us both in the language and images they use.Among them we find the American poet Robert Frost. More and more people are interested to read modern poetry in English.Translation can be good,but being able to read English gives you much choice.Besides,no matter how well a poet is translated,something of the spirit of the original work is lost.Reading poetry in English also opens the door to finding new ways of expressing yourself in Chinese. Ⅱ.What is free verse? Free verse is a modern form of poetry which does not follow any specific rhyme or metrical scheme,although it does not completely abandon the basic poetic precepts of heightened language and songs.Free verse poetry is said to have been popularized by such notable poets as Walt Whitman and Emily Dickinson during the late 19th century,although earlier poets like the mystic William Blake were beginning to pull away from the restrictions of the formal poetry of their day.Whitman's signature collection,Leaves of Grass,is almost entirely composed of free verse poetry.Dickinson,however,still wrote much of her poetry according to the metrics and rhyme of a favored hymn composer. The free verse style of poetry soon became popular with rebellious young poets such as the Frenchman Artur Rimbaud(阿图尔·兰波),who wrote many of his best free verse poems before the age of 18.Other poets embraced free verse poetry as a way to express raw emotions or unbridled passion not generally found in the formal poetry of their time.Whitman himself referred to this artistic awakening as the great YAWP,a call for all artists to break free of social conventions and live life to its fullest. Free verse poetry continued to evolve throughout the 20th century,beginning with poets such as Carl Sandburg(卡尔·桑博格)and Robert Frost(罗伯特·弗罗斯特),both of whom were equally comfortable with formal and free verse poetry.Perhaps the most admired free verse poet was the expatriate Ezra Pound,who became a mentor to many of the 20th century's most famous authors and poets. Period 2 Language Study 整体设计 教学内容分析 The emphasis of this period will be placed on the important new words,phrases and sentence patterns in Warming Up,Pre-reading,Reading,Comprehending and Discovering useful words and expressions in Learning about Language.There are altogether 50 new words and phrases in these five parts.22 of them are marked with triangles,which shows that the students needn't learn them by heart.It is enoug h to recognize them when meeting them while reading the passage.The other 28 should all be remembered,among which the following 8 words and expressions are even more important:concrete,take it easy,in particular,flexible,eventually,transform,run out of,be made up of. They are all very useful and important.So are the sentence patterns “Some poems tell a story or describe something in a way that will give the reader a strong impression.”,“Some rhyme(like B) while others do not(like C).” and “Another simple form of poem that students can easily write is the cinquain,a poem made up of five lines.” We ought to pay more attention to them. 三维目标设计 Knowledge and skills 1.To get the students to learn to use the following important new words and phrases freely:rhyme,concrete,pattern,tease,endless,translation,take it easy,in particular,convey,flexible,branch,eventually,transform,forever,run out of,be made up of. 2.To get the students to understand and use the following important and useful sentence patterns: (1)Some poems tell a story or describe something in_a_way_that_will_give_the_reader_a _strong_impression. (2)Some rhyme(like B) while others do not(like C). (3)Another simple form of poem that students can easily write is the cinquain,a poem made_up_of_five_lines. Process and methods 1.To help the students to understand the meanings of the above useful new words and expressions in the context,and then give some explanations about them,and at last offer some exercises to make the students master their usages. 2.To ask the students to make up their own sentences by imitating the above sentence patterns. 3.At t he end of the class,make students do more exercises for consolidation.In doing so,they can learn,grasp and use these important language points well. Emotion,attitude and value 1.To stimulate students' interest in learning English. 2.To develop students' sense of cooperation and teamwork. 教学重、难点 1.Important new words and expressions:rhyme,concrete,pattern,tease,endless,translation,take it easy,in particular,convey,flexible,branch,eventually,transform,forever,run out of,be made up of. 2.Important and useful sentence patterns: (1)The attributive clause with the antecedent “way”. (2)Compound sentences with “while”. (3)Past participles as the postpositive attributive. 3.Some difficult and long sentences in the text. 教学过程 Step 1 Revision 1.Check the homework exercises. 2.Ask some students to tell about some simple forms of English poems. Step 2 Reading and finding Get students to read through Warming Up,Pre-reading,Reading,Comprehending and Discovering useful words and expressions in Learning about Language to underline all the new words and useful expressions or collocations in these parts.Read them aloud and copy them down in the exercise book. Step 3 Practice for useful words and expressions 1.Turn to Page 12.Go through the exercises in Discovering useful words and expressions with students and make sure they know what to do. 2.Give them several minutes to finish the exercises.They may first do them individually,and then discuss them with their partners. 3.Check the answers with the whole class and explain the problems they meet where necessary. Step 4 Vocabulary study Ⅰ.简单知识扫描 1.poem/poetry(P9) Poet(P10) 【原句再现】 These little poems and songs might have been some of the first poetry you learned. 这些小诗歌或许就是你最早学到的一些诗歌。 Poets use many different forms of poetry to express themselves. 诗人用许多不同格式的诗来表达自己的情感。 【归纳总结】 poem n.诗;诗歌[C]一首诗 a poem poetry n. [U](总称)诗歌,韵文 poet诗人 【即景活用】用poet,poem,poetry填空: (1)As a piece of ______,it seems to be a selection of the Renaissance. (2)He is both a soldier and a ______. (3)I decided to write a ______ about what I felt. Suggested answers:(1)poetry (2)poet (3)poem 2.rhyme(P9) 【原句再现】 Which poem has rhyming words at the end of lines? 哪首诗在每行后有押韵的词? 【观察探究】 (1)This poem doesn't rhyme.这首诗不押韵。 (2)Shakespeare sometimes wrote in rhyme.莎士比亚有时用韵文写作。 (3)What words rhyme with “school”? 哪些词和“school”押韵? (4)You can rhyme “hiccups” with “pick-ups”. 用“hiccups”可和“pick-ups”押韵。 【归纳总结】 rhyme n. 韵,押韵,韵文 vt. 押韵,用韵诗表达 vi. 押韵 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)我对这首摇篮曲很熟悉。 (2)这首诗的最后两行没有押好韵。 Suggested answers:(1)This nursery rhyme is very familiar to me. (2)The last two lines of this poem don't rhyme properly. 3.concrete(P10) 【原句再现】 The language is concrete but imaginative,and they delight small children because they rhyme,have strong rhythm and a lot of repetition. 童谣的语言具体但富有想象力,这能使小孩子们快乐,因为它们押韵,节奏感强,并较多重复。 【观察探究】 (1)Have you any concrete thoughts on how to deal with this difficulty? 处理这种困难你有什么具体的想法? (2)The word “apple” is a concrete noun.“苹果”是个具体名词。 (3)His plan is not yet concrete.他的计划尚不具体。 (4)These buildings are made of concrete and steel. 这些房屋是用钢和混凝土建成的。 【归纳总结】 concrete adj.具体的n.混凝土 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)鞋和树是实物。 (2)你有没有具体的建议呢? Suggested answers:(1)Shoes and trees are concrete objects. (2)Have you got any concrete proposals? 4.pattern(P10) 【原句再现】 List poems have a flexible line length and repeated phrases which give both a pattern and a rhythm to the poem. 清单诗可长可短,可以重复一些短语,较为灵活,形成固定句型和诗的节奏。 【观察探究】 (1)The illness is not following its usual pattern. 这种病不是它通常的症状。 (2)Does the poem have a rhythmic pattern?这首诗有韵律吗? (3)Her ideas are patterned on Trotsky's.她的思想是仿效托洛茨基的。 【归纳总结】 pattern n.模式、方式、形式;图案 ;模范,榜样;v.模仿 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子,体会pattern 在句中的用法: (1)She wore a dress with a pattern of roses on it. (2)The company set a pattern for others to follow. (3)He patterned himself upon a man he admired. Suggested answers:(1)她穿了一件有玫瑰图案的礼服。 (2)这家公司为其他公司树立了典范。 (3)他模仿他崇拜的那个人。 5.tease(P11) 【原句再现】 Brother Beautiful,athletic Teasing,shouting,laughing Friend and enemy too Mine 兄弟 爱美,又爱运动 爱闹,爱叫,又爱笑 是我的朋友 也是我的敌人 【观察探究】 (1)At school the other children always teased me because I was fat. 在学校里别的孩子总是取笑我,因为我很胖。 (2)They teased her about her laziness.他们笑她懒惰。 (3)Don't take it seriously—he was only teasing. 别当真,他只不过是在开玩笑。 (4)Stop teasing the poor cat! 不要捉弄那只可怜的猫了。 (5)He's a terrible tease.他特别爱戏弄人。 【归纳总结】 tease v. 取笑,招惹,戏弄; n. 爱开玩笑的人,爱戏弄别人的人 tease sb./sth. 取笑,招惹,戏弄(某人/某物) 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)她总是戏弄别人。她真是爱捉弄人! (2)虽然你的同桌有点胖,你也不准嘲笑她。 Suggested answers: (1)She always laughs at others.What a tease she is! (2)Although your deskmate is a little fat,you must not tease her. 6.endless(P11) 【原句再现】 Summer Sleepy,salty Drying,drooping,dreading Week in,week out Endless 夏天 困乏,咸涩 干涸,枯萎,恐怖 周而复始[来源:学科网] 永无止境 【观察探究】 (1)I began to sicken of the endless violence shown on television. 我逐渐对电视上无休无止的暴力镜头感到厌恶。 (2)The fascinations of the circus are endless. 马戏表演非常吸引人。 (3)Visitors to the exhibition came in an endless stream. 参观展览会的人络绎不绝。 (4)The endless lea will purify your thought. 一望无际的草原会净化你的思想。 【归纳总结】 endless adj. 无止境的,没完没了的 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)这旅程仿佛是无穷无尽的。 (2)我讨厌他不断的打扰。 Suggested answers:(1)The journey seemed endless. (2 )I am tired of his endless interruptions. 7.translation(P11) 【原句再现】 The two haiku poems(F and G) above are translations from the Japanese. 上面的两首俳句诗(F篇和G篇)就是从日文翻译出来的。 【观察探究】 He has an English translation of Marx's Capital.他有马克思的《资本论》的英语译文。 【知识链接】 (1)When people are learning a foreign language,they should not translate everything into their own language. 当人们学习一门外语的时候,他们不应该把什么东西都翻译成他们自己的语言。 (2)Can you translate these ideas into reality? 你能将这些思想变成行动吗? (3)Her novels translate well. 她的小说翻译得很好。 【归纳总结】 translation n.翻译;译文 translate vt.& vi.翻译,把……用另一种形式表达出来;能被翻译 translate...into...把……译成…… 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)A lot of Tang poems has been translated into English. (2)Most poems don't translate well. (3)The sentence won't translate. (4)It's time to translate your idea into action. Suggested answers: (1)很多唐诗已被翻译成了英语。 (2)大多数诗歌译得不好。 (3)这个句子不能翻译。 (4)该是你行动的时候了。 8.take it easy(P10) 【原句再现】 We would have won if we hadn't taken_it_easy. 如果我们没有放松警惕的话,我们本来是会夺冠的。 【观察探究】 (1)Sit down and take it easy.坐下来,放松会儿。 (2)Just take it easy and tell us exactly what happened. 别紧张,告诉我们究竟发生了什么。 【归纳总结】 take it easy 沉住气,不紧张,慢慢来 【知识链接】 take one's time慢慢来,不急;拖拉,慢吞吞 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)The doctor told me to take things easy and stop working so hard. (2)There's no hurry;take your time. Suggested answers: (1)大夫让我别紧张,不要干得这么辛苦。 (2)不急,慢慢来。 9.in particular(P11) 【原句再现】 Did you know that English speakers also enjoy other forms of Asian poetry—Tang poems from China in_particular? 你知道吗?说英语的人也喜欢其他类型的亚洲诗,尤其是中国的唐诗。 【观察探究】 (1)He studies in particular the fishes of the Indian Ocean. 他专门研究印度洋的鱼类。 (2)I noticed his eyes in particular,because they were such an unusual colour. 我尤其注意到他的眼睛,因为它们的颜色非同寻常。 【归纳总结】 in particular尤其,特别 【即景活用】 根据汉语意思,用恰当的短语填空。 (1)她特别强调了那一点。 She stres sed that point______. (2)工程技术人员尤其必须能够迅速而准确地将自己的想法传达给别人。 The engineer ______ must be able to communicate his ideas to others rapidly and accurately. Suggested answers:(1)in particular (2)in particular Ⅱ.重点知识探究 1.convey(P10) 【原句再现】 Others try to convey certain emotions. 而有些诗则是为了传达某种感情。 【观察探究】 (1)convey a sense/an impression/an idea etc.表达(感觉、感情、意见、思想等) (2)He was sent to convey a message to the U.N.Secretary General. 他被派去向联合国秘书长传达信息。 (3)I want to convey to children that reading is interesting. 我想向孩子们传达这样的思想:读书是很有趣的。 (4)Wires convey electricity from power stations to the users. 电线把电从电厂传送到用户。 (5)The government conveyed this piece of land to a company. 政府把这块土地转让给了一家公司。 【归纳总结】 convey v.传达,表达(感情,意见,思想等) convey sth.to sb.把……传达给……;把(土地、财产等)转让给…… convey sth.from...to...把……从……传送/运送到…… 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)这火车既运送乘客也运输货物。 (2)言语无法表达我当时是多么高兴。 (3)请向你父母转达我最美好的祝愿。 Suggested answers: (1)This train conveys both passengers and goods. (2)Words can't convey how delighted I was. (3)Please convey my best wishes to your parents. 2.flexible(P10) 【原句再现】 List poems have a flexible line length and repeated phrases which give both a pattern and a rhythm to the poem. 清单诗可长可短,可以重复一些短语,较为灵活,形成固定句型和诗的节奏。 【观察探究】 (1)We need a foreign policy that is more flexible. 我们需要一个更为灵活的外交政策。 (2)This tube is flexible but tough. 这管子柔软但很坚固。 【归纳总结】 flexible adj.灵活的,易弯曲的,柔韧的,可变通的 【即景活用】 根据汉语意思,用恰当的词填空。 (1)橡皮管可以弯曲。 A piece of rubber hose is______. (2)柔性管道便于在紧凑的空间安装。 ______ tubing can assist in installation in tight space. Suggested answers:(1)flexible (2)Flexible 3.branch(P11) 【原句再现】 A fallen blossom is coming back to the branch. 落下的花朵回到 了树枝上。 【观察探究】 (1)The bank has ten branches in the city. 这家银行在市内有十家分行。 (2)Many birds are on the branch. 很多鸟栖息在树枝上。 (3)The river has a lot of branches. 这条河有很多支流。 (4)Physics is a branch of science. 物理学是科学的一门分支学科。 (5)Mary has left the company and branched out her own. 玛丽离开公司做起了自己的生意。 【归纳总结】 branch n. 枝条;支流;(学科的)分科,部门;支部,分部;vt.& vi.分支,分岔 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)The company's head office is in the city,but it has ______(部门) all over the country. (2)______(路分叉)where the tall building stands. (3)______(党小组) were completely destroyed then. Suggested answers:(1)branches (2)The road branches (3)The party branches 4.eventually(P11) 【原句再现】 With so many different forms of poet ry to choose from,students may eventually want to write poems of their own. 有了这么多可供选择的诗歌类型,学生们最终也许想自己写诗了。 【观察探究】 (1)She eventually married the most persistent one of her admirers. 她终于嫁给了最执著追求她的人。 (2)After playing the part for over 20 years,she was eventually written out(of the series). 她扮演了20多年的一个角色,最后(从连续剧中)去掉了。 (3)I was eventually granted an exit visa.我终于获得了出境签证。 (4)He struggled with his assailants and eventually drove them off. 他同攻击他的人进行搏斗,最后把他们赶走了。 (5)It was a long journey,but we eventually arrived. 旅程很长,但我们最后还是到达了。 【归纳总结】 eventually adv.终于,最后 【即景活用】 根据汉语意思,用恰当的词填空。 (1)该政府终于在1970年倒台了。 The government ______collapsed in 1970. (2)他工作太努力了, 最后竟病倒了。 He worked so hard that ______he made himself ill. Suggested answers:(1)eventually (2)eventually 5.transform(P11) 【原句再现】 Never looking back, transformed_into stone.化为石,不回头。 【观察探究】 (1)A fresh coat of paint can transform a room. 房间重新粉刷一遍可大为改观。 (2)The wizard transformed the prince into a frog. 巫师把王子变成了青蛙。 【知识链接】 His character has undergone a great transformation since his failure in marriage. 自婚姻失败以来,他的性格已有重大改变。 【归纳总结】 transform vt.改变(……的形状,外观,品质或性质) transform sth.(into sth.)把……变成…… transformation n.变革,改变 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)Success and wealth transformed his character. (2)A steam-engine transforms heat into energy. (3)He transformed the garage into a recreation room. (4)His plans were tr ansformed overnight into reality. (5)在过去的十年里,我们的工作方式经历了彻底的变革。 Suggested answers:(1)成功和财富改变了他的性格。 (2)蒸汽机把热变成能。 (3)他把车库改造成了娱乐室。 (4)他的计划迅速成为现实。 (5)The way in which we work has undergone a complete transformation in the past decade. 6.forever(P12) 【原句再现】 something that seems to last forever似乎是永远持续下去的某种东西 【观察探究】 (1)Many Pharaohs in ancient Egypt believe they can live forever. 古埃及的许多法老相信他们可以永生。 (2)You'll never see life if you stay at home forever. 如果你一直待在家里,就永远不会有生活经验。 【归纳总结】 forever adv.永远;老是,不断地 【即景活用】 根据汉语意思,用恰当的词填空。 (1)祝两国人民的友谊万古长青! May the friendship between the peoples of(our)two countries last______! (2)民族英雄永远活在我们心里。 The national heroes will live ______ in our hearts. Suggested answers:(1 )forever (2)forever 7.run out of(P10) 【原句再现】 We would have won if we hadn't run_out_of energy. 我们本来会夺冠,如果我们没有精疲力竭。 【观察探究】 (1)It is very important that this organization does not run out of money. 这个组织没有用光钱,这是很重要的。 (2)We've run out of petrol.What a bore! 我们的汽油用完了。真麻烦! 【归纳总结】 run out of“用光;耗尽”。 【知识链接】 run out与 run out of 的辨析 (1)run out是“动副型”短语动词,作不及物动词,表示被动含义,意为“被用完了(become used up)”,其主语通常是时间、金钱、食物等无生命名词。例如: Could I have a cigarette? I seem to have run out. 给我一枝烟好吗? 我的(烟)好像已经抽完啦。 (2)run out of 是三个词组成的短语动词,作及物动词用,后接宾语,表示主动含义,意为“用完(use up)”,其主语只能是人。例如: What if/Say y ou were to run out of money? What would you do? 假设你的钱用完了呢?你会怎么办呢? (3)run out of还有“从(某处)流出(跑出)”的意思;run out也有“流出,跑出”的意义,但其后不能接宾语。 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)他的钱很快就花完了。 (2)逛完街我的钱用光了。 (3)他跑出了房间。 (4)如果我们的糖没有用完,我就不会去商店了。 Suggested answers: (1)His money soon ran out. (2)I ran out of money after I finished shopping. (3)He ran out of the room. (4)If we hadn't run out of sugar,I wouldn't have gone to the shops. 8.(be)made up of(P10) 【原句再现】 Another simple form of poem that students can easily write is the cinquain,a poem made_up_of five lines. 另外一种学生容易写的简体诗是由五行组成的,叫五行诗。 【观察探究】 All bodies are made up of atoms. 一切物体都是由原子组成的。 【归纳总结】 be made up of 由……组成/构成 【知识链接】 (1)make up ①弥补;补偿;补足;补(考) ②整理(房间等);准备(床铺等) ③调停;和解 ④虚构;捏造 ①He made up some excuse about his daughter being sick. 他编造了个借口,说他的女儿病了。 ②Can I leave early this afternoon and make up the time tomorrow? 我今天下午早点走,明天补上这段时间,可以吗? ③Has she made it up with him yet? 他们和解了吗? ④We made up the bed in the spare room.我们在空屋里搭了张床。 (2)make up for补偿 ①How can we make up to you for what you have suffered? 我们如何补偿你所遭受的损失? ②make up for lost time补回失去的时间 ③They hurried on to make up for lost time. 他们加速进行以补回失去的时间。 【即景活用】 辨别下列各句中make up的意义。 (1)They quarreled(with each other)but soon made up. (2)She made up her face to look prettier. (3)The boy made up a story;it was not true. (4)We need one more player to make up a team. Suggested answers:(1)和解;和好 (2)化妆 (3)虚构;捏造 (4)补足;凑足 Ⅲ.词汇综合运用 1.用括号中所给的单词或短语 翻译下列句子。 (1)我过去常去看电影,可现在总是抽不出时间来。(used to) (2)他们都累得只会打哈欠了。(so...that) (3)我难以想象我会娶那种姑娘。(imagine) (4)她在茶中加了些糖。(add) (5)课后尽量多练习讲英语。(as...as) (6)这完全是偶然发生的。(by chance) Suggested answers: (1)I used to go to the cinema a lot,but I never get the time now. (2)They were all so tired that they could do nothing but yawn. (3)I can't imagine my marrying a girl of that kind. (4)She added sugar to her tea. (5)Please practice speaking English as much as you can after class. (6)It happened quite by chance. 2.根据汉语提示,完成下列句子。 (1)The suitcase ______ ______(制成)leather is square. (2)______(虽然)tired,she kept waiting. (3)I can't ______(赢得)his friendship,though I've tried. (4)All our supply of food ______ ______ ______(用完了). (5)If ______ ______ ______(没有)air,there would be no life on the earth. Suggested answers: (1)made of (2)Though (3)win (4)has run out (5)there were no Step 5 Sentence focus 1.Some poems tell a story or describe something in a way that will give the reader a strong impression.(P10) 有的诗歌讲述一个故事或用一种能给读者深刻印象的方式来描述某件事。 在这个复合句中,含有一个由that引导的定语从句,that在从句中作主语,修饰名词way。和下面两个句子比较一下,看有什么区别。 ①I feel surprised at the way in_which/that/不填he talks to his mother. ②In 1770,the room was completed the way_in_which/that/不填she wanted it. 2.Some rhyme while others do not.(P10) 清单诗有些押韵,有些不押韵。 这是由while引导的并列句。while意思是“然而;可是” ,表示对比。 试着翻译一个句子: 他是医生,而我是老师。(He is a doctor while I am a teacher.) while还有很多常见的含义,猜测它在下面各句中的含义并写出选项。 A.只要 B.然而 C.虽然;尽管 D.当……时候 ①While I understand what you say,I can't agree with you.______ ②My wife kept silent while I was writing.______ ③Strike while the iron is hot.______ ④While there is life there is hope.______ ⑤Their country has plenty of oil,while ours has none.______ Suggested answers:①C ②D ③D ④A ⑤B 3.Another simple form of poem that students can easily write is the cinquain,a poem made up of five lines.(P10) 另外一种学生容易写的简体诗是由五行组成的,叫做五行诗。 这是一个倒装句,全句的主语是another simple form of poem。that从句是定语从句,修饰poem。在逗号后a poem是名词作同位语,是对前面的名词the cinquain的解释说明。过去分词短语made up of作定语,修饰前面名词a poem,相当于一个定语从句which is made up of five lines. Step 6 Homework 1.Finish off the Workbook exercises in Using Words and Expressions.Do Exercise 3 in your exercise book. 2.Learn the useful new words and expressions by heart. Step 7 Reflection after teaching Period 3 Grammar—the Subjunctive Mood(2) 整体设计 教学内容分析 This teaching period mainly deals with the grammar:the subjunctive mood(2).From Unit 1 we have already known that i n the English language,verbs are often divided into three different moods—the indicative mood,the imperative mood and the subjunctive mood.We have learned two kinds of subjunctive mood in Unit 1:one is found after the word “wish”,the other is found in a clause beginning with the word “if” talking about the imagined consequence of a situation at present that is impossible to happen.In this period we will continue to focus on another kind of subjunctive mood,that is,the subjunctive mood beginning with the word “if”,talking about the imagined consequence of a situation in the past that did not happen or in the future that is not likely to happen. 三维目标设计 Knowledge and skills 1.To get the students to know the structure of the subjunctive mood. 2.To let the students learn the usages of the subjunctive mood. 3.To enable the students to use the subjunctive mood correctly and properly. Process and methods 1.To ask the students to read the reading passage again,pick out the sentences with the subjunctive mood and translate them into Chinese. 2. To ask the students to discover the structure and usages of the subjunctive mood by comparing a lot of example sentences. 3.To ask the students to do the exercises in Discovering useful structures on Page 13 to master the subjunctive mood. 4.To ask the students to summariz e the usages of the subjunctive mood. 5.To ask the students to do the exercises in Using Structures on Pages 50-51 and some other additional exercises for consolidation. Emotion,attitude and value 1.To get the students to become interested in grammar learn ing. 2.To develop the students' ability of comparing and summarizing. 教学重、难点 1.To get the students to master the structure and usag es of the subjunctive mood. 2.To enable the students to learn how to use the subjunctive mood correctly. 教学过程 Step 1 Revision 1.Check the homework exercises. 2.Dictate some new words and expressions. 3.Translate the following sentences into English: (1)我们的时间快用完了。 (2)他编造了滑稽的顺口溜引逗我们发笑。 Suggested answers: (1)We are running out of our time. (2)He made up funny rhymes to make us laugh. Step 2 Warming up Ask the students to go back to Page 10 and study one of the list poems,Poem C Our First Football Match and translate it into Chinese,paying special attention to its verb forms: We would_have_won ... if Jack had_scored that goal, if we'd_had just a few more minutes, if we had_trained harder, if Ben had_passed the ball to Joe, if we'd_had thousands of fans screaming, if I hadn't_taken my eye off the ball, if we hadn't_stayed_up so late the night before, if we_hadn't_taken it easy, if we hadn't_run out of energy. We would_have_won ... if we'd_been better! Tell the students that the above sentences are with the subjunctive mood and then discuss it with them.Then ask the students to think about the question “What is the subjunctive mood?” Step 3 Grammar learning Ask the students to study the following sentences and try to summarize the structure and usages of the subjunctive mood. 1.The subjunctive mood in the past tense: (1)I could have done better if I had been more careful. 我要是细心一点,是可以做得更好的。 (The fact is that I was not more careful and I didn't do better.) (2)I could have shown you around the city if I had known you were in Beijing. 我要是早知道你在北京,我就会带你到处去转转。 (The fact is that I didn't know you were in Beijing and I didn't show you around the city.) (3)If I had been in the mood,I would have gone to the movies. 如果我有心情的话,我就会去看电影了。 (The fact is that I was not in the mood and I didn't go to the movies.) 2.The subjunctive mood in the future tense: (1)从句谓语用过去式: If your fat her knew this,he would be angry. 要是你父亲知道了,他会生气的。 If it rained tomorrow,the sports meet would be put off. 要是明天下雨,运动会就会被推迟。 (2)从句谓语用should+动词原形(通常指可能性极小的事情,一般译为“万一”): If it should rain,the crops would be saved. 要是有雨,这庄稼还有救。 此类句型的主句谓语有时可以用祈使句甚至将来时态: If it should rain tomorrow,don't expect me. 万一明天下雨,就不要等我了。 If I sh ould be free tomorrow,I will come. 万一我明天有空,我就来。 (3)从句谓语用were to+动词原形(通常指可能性极小或近乎不可能,有时指出乎意料): If the sun were to rise in the west,my love for you would not change. 即使太阳从西边升起,我对你的爱也不会变。 Step 4 Summing up Try to help the s tudents draw the following conclusions: 1.The subjunctive mood is usually used to talk about situations that are not true or not likely to be true.The situation referred to in the subjunctive mood is not real,but it is hypothetical. 2.The subjunctive mood is often found in a clause beginning with the word “if”.The past perfect tense(had done/been)is often used in the “if” clause and “would+have done/been” is often used in the main clause expressing the situation contrary to the past. 3.In expressing the situation contrary to the future,“were/did/should+v./were to+v.” is often used in the “if” clause and “would+v.” is often used in the main clause expressing the situation contrary to the future. Step 5 Grammar practice Ask students to do the following exercises: 1.Change the following sentences into the subjunctive mood.Put the verbs into the correct forms. (1)She was busy,so she didn't come. (2)We didn't know your telephone number,so we didn't call you. (3)Everybody who ate the fish got sick.I didn't eat any fish. Suggested answers: (1)If she hadn't been busy,she would have come. (2)If we had known your telephone number,we might have called you. (3)If I had eaten the fish,I would have gotten sick too. 2.Do Exercise 3 in Discovering useful structures on Page 13. 3.Do the exercises in Using Structures on Pages 50-51. First ask students to do the exercises individually,and then let them discuss and check their answers with their partners,and finally give them the correct answers and deal with any problems they might meet. Step 6 Getting more about the grammar Ask students to go back to Page 10 and read through the reading passage A Few Simple Forms of Englis h Poems to pick out the sentences with the subjunctive mood and then translate them into Chinese. Suggested answers: We would_have_won... 我们本来会夺冠…… if Jack had_scored that goal, 如果杰克踢进了那个球, if we'd_had just a few more minutes, 如果我们还有几分钟, if we had_trained harder, 如果我们训练得更严格, if Ben had_passed the ball to Joe, 如果本把球传给了乔, if we'd_had thousands of fans screaming, 如果有大批球迷助威, if I hadn't_taken my eye off the ball, 如果我死死盯住球, if we hadn't_stayed_up so late the night before, 如果我们头晚不熬夜, if we_hadn't_taken it easy, 如果我们没有放松警惕, if we hadn't_run out of energy. 如果我们没有精疲力竭, We would_have_won... 我们本来会夺冠…… if we'd_been better! 如果我们能干得更好! Step 7 Summing up Try to help the students draw the following conclusions. 1.When the subjunctive mood is found in a clause beginning with the word “if”,“had been+past participles” is used in the “if” clause,while “would/could have+past participles” is used in the main clause so as to express the situation contrary to the past. 2.In sentences with the subjunctive mood,sometimes a prepositional phrase beginning with “without(=if not)” is used to take the place of the “if” clause to express implied condition. Step 8 Playing a game 1.Get students to form groups of 6. 2.Let students play the game “We would have won the championship if we...” Ask the students to take turns to imagine what they would have done to win the championship.Make their own sentences as interesting and imaginative as they can.Write down the six best ones and share them with the class. 3.Read the following composition and try to find out as many sentences with the subjunctive mood as possible. Unexpected Guests Linda had a very difficult situation at her house a few days ago.Her relatives from Hong Kong arrived unexpectedly,without any advance notice at all,and they wanted to stay for the weekend.They didn't even knock at the door.They just walked right in. Needless to say,Linda was very upset.If she had known that her relatives from H.K.were going to arrive and want to stay for the weekend,she would have been prepared for their visit.She would have bought a lot of food.She would have cleaned the house.She would have made plans to go sightseeing.She would have cooked a special dinner.She would have planned everything perfectly.And she certainly wouldn't have invited all her daughter's friends from nursery school to come over and play. Poor Linda! She really wishes her relatives had called in advance to say they were coming.The weekend was really a disaster! Suggested answers: Unexpected Guests Linda had a very difficult situation at her house a few days ago.Her relatives from Hong Kong arrived unexpectedly,without any advance notice at all,and they wanted to stay for the weekend.They didn't even knock at the door.They just walked right in. Needless to say,Linda was very upset.If she had_known that her relatives from H.K.were going to arrive and want to stay for the weekend,she would_have_been_prepared for their visit.She would_have_bought a lot of food.She would_have_cleaned the house.She would_have_made plans to go sightseeing.She would_have_cooked a special dinner.She would_have_planned everything perfectly.And she certainly wouldn't_have_invited all her daughter's friends from nursery school to come over and play. Poor Linda! She really wishes her relatives had_called in advance to say they were coming.The weekend was really a disaster! Step 9 Closing down by a quiz Show students the following on the screen or give out test papers to them. 1.You are late.If you ______ a few minutes earlier,you ______ him. A.come;would meet B.had come;would have met C.come;will meet D.had come;would meet 2.Let's say you could go there again,how ______ feel? A.will you B.should you C.would you D.do you 3.If you had told me in advance,I ______ him at the airport. A.would meet B.will meet C.would have met D.will have met 4.I would have told him the answer had it been possible,but I ______ so busy then. A.had been B.were C.was D.would be 5.If it ______ another ten minutes,the game would have been called off. A.had rained B.would have rained C.have seen D.rained 6.—Why didn't you buy a new car? —I would have bought one if I ______ enough money. A.had B.have had C.would have D.had had 7.He was very busy yesterday;otherwise,he ______ to the meeting. A.would come B.came C.would have come D.will come 8.______ any change about the date,please tell me immediately. A.Will there be B.Should there be C.There will be D.There should be 9.A few minutes earlier and we ______ the train. A.have caught B.had caught C.could have caught D.were to catch 10.If the Watergate Incident ______,Nixon would not have resigned from the presidency. A.did not occur B.had not occurred C.was not occurring D.be circling 11.If I had seen the movie,I ______ you all about it now. A.would tell B.will tell C.have told D.would have told Suggested answers: 1~5 BCCCA 6~10 DCBCB 11.A Step 10 Homework 1.Finish off the Workbook exercises. 2.Preview listening and speaking. Step 11 Reflection after teaching ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Period 4 Listening and Speaking 整体设计 教学内容分析 The emphasis of this period will be placed on listening and speaking.There are altogether three texts for the students to listen to in this period:one is in the Student's Book and the other two are in the Workbook.The first one(on Page 15,Listening and speaking)is a conversation between a teacher and three of her students,Lucy,Pitt and Jack.They are talking about a poetry competition.The students talk about when they are going to write their poems and how they become inspired to write poetry.Their discussion illustrates the function of intention.While listening to Part 1 of the dialogue for the first time the students are asked to get some specific information about it and answer four wh-questions.After listening to the second part of the dialogue for the first time the students are asked to get more detailed information and fill in the chart.At last the students are asked to listen to the whole passage again and note down the expressions about intention and plans. The second one(on Page 48,Listening)is a conversation between a teacher and three of his stu dents,Wu Zhe,Lily and Chelsea.They are discussing how they feel about listening to poetry and writing it.They also discuss how they go about writing poetry.The teacher's opening question is an example of the third conditional.And the third one(on Page 53,Listening Task)is a conversation between three students about their poetry homework.They are talking about the kin d of poem each is going to write.In their discussion,the students use expressions of intention,the focus function of the unit. 三维目标设计 Knowledge and skills 1.To understand the meanings of the following key words and expressions while hearing them in the tape:deadline(最后期限,截止时间),go for a hike(去徒步旅行),atmosphere(气氛),create(创造,造成),spill out(溢出,流),horrible(可怕的,令人讨厌的). 2.To enable the students to understand the listening texts. 3.To help the students learn how to express their intention and plans. Process and methods 1.Smoothing away language problems if any before listening. Before asking the students to listen to the tape,help them to smooth away any language problems such as new words and expressions that they may not understand while listening. 2.Listening for needed information. Before asking the students to listen to the tape for the first time,give them one or two questions about the general idea of the text so as to lead the students to concentrate only on the needed information.Then ask them to listen to the tape for a second or even a third time for some specific information by giving them some detailed questions to answer. 3.Speaking freely and making conversations. At last the students may be asked to give their own points of view and attitudes towards certain subject mentioned in the text. Emotion,attitude and value 1.To arouse the students' curiosity about poems. 2.To develop the students' sense of exploring. 3.To cultivate the students' sense of cooperative learning in a group. 教学重、难点 1.The understanding of the listening texts. 2.The exp ressing of intention and plans. 教学过程 Step 1 Revision 1.Retell the text on Page 10-Page 11. 2.Check the answers of the exercises in Learning about Language and explain the difficulties. Step 2 Listening 1.Listen to Text 1(Page 15)and do the following exercises. (1)Listen to the tape and write down the main idea of the listening material. ________________________________________________________________________ (2)Listen to the tape again then choose the best answers. ①What's the deadline for the poetry competition? A.20th. B.22nd. C.24th. ②How is Pitt going with his poem? A.He has already written something. B.He is not going to enter a poem this year. C.He is going to write one this weekend. ③What is Jack going to do? A.He will go on a hike into the countryside. B.He will catch insects in the grass. C.He will pick wild flowers. ④What is Lucy going to do? A.She will be surrounded by familiar things. B.She will stay in her house. C.She will try out Jack's way some time. ⑤How can Pitt work best? A.When he is going on a hike. B.When he is listening to his favorite music. C.When he is watching beautiful flowers. (3)Listen to the tape and fill in the blanks. Well,I______ a lot more—maybe an insect in the grass ______something,the shapes and ______of the flowers,how the wind sounds,or the ______smells in the air.______,I find that as I look around me all sorts of interesting ______and words come into my head. I write best when I'm ______by familiar things,so I ______to be in my house.And it needs to be very______.But now I've ______to Jack,I think I'll also ______his way some time. (4)Use one sentence to tell how each one of them is getting on with his or her task. Jack ________________________________________________________________________ Lucy ________________________________________________________________________ Pitt ________________________________________________________________________ Suggested answers: (1)The teacher tells Lucy,Pitt and Jack how to become inspired to wr ite poetry. (2)①C ②B ③A ④C ⑤B (3)notice,carrying,colors,different,Anyway,thoughts;surrounded,need,quiet,listened,try out. (4)Jack will go on a hike to get some inspiration. Lucy has written something. Pitt is going to try one out tonight. 2.Listen to Text 2(Page 48)and do the following exercises. (1)Listen to the conversation and answer the following two questions. ①Who enjoys listening to poetry? ②Who enjoys writing poetry? (2)Listen to the conversation again and match each student with the reason he or she enjoys or doesn't enjoy poetry.There are two reasons for each person. WU ZHE Poetry is like music. It's rubbish. LILY I like playing with words. The language in poetry is strange. CHELSEA Poetry takes you to a different world. You don't have to follow grammar rules. (3)Listen to the tape again and match each student with the words they said and note the different feelings of the three students about poetry when they say the following words. LILY My heart sinks! Poetry,yuck! WU ZHE I love listening to it too...But I'd much rather be writing it. CHELSEA Sometimes I feel inspired and the right words just come spilling out. Suggested answers: ( 1)①Lily and Chelsea. ②Lily and Chelsea. (2)WU ZHE It's rubbish. The language in poetry is strange. LILY Poetry is like music. Poetry takes you to a different world. CHELSEA I like playing with words. You don't have to follow grammar rules. (3)LILY Sometimes I feel inspired and the right words just come spilling out.(enthusiastic) WU ZHE My heart sinks! Poetry,yuck!(resentful) CHELSEA I love listening to it too...But I'd much rather be writing it.(cheerful) 3.Listening task on Page 53. Before listening,ask the students to read Exercise 1 so that they know the pieces of information they have to listen for. (1)Listen to the conversation and judge whether the following statements are true(T)or false(F). ①The students have to give their poetry homework to the teacher today. ②Sam is going to write his poem on the weekend. ③Sam doesn't like the poetry homework. ④Sally doesn't want to do her poetry homework. ⑤Sam doesn't remember what a haiku is. ⑥Ben is going to the park on Saturday. ⑦Sam is going to write a poem about himself. ⑧Sally,Ben and Sam are all present at the beginning of the conversation. (2)Listen to the tape again and fill in the chart below. Questions Sam Ben Sally What kind of poem is the student going to write? What topic is the student going to write about? Suggested answers: (1)①F ②T ③T ④F ⑤T ⑥T ⑦F ⑧F (2) Questions Sam Ben Sally What kind of poem is the student going to write? cinquain haiku list poem What topic is the student going to write about? Ben nature the students in her class Step 3 Speaking Since the students have learned much knowledge about poetry by both reading and listening.It's necessary for them to talk about it now.Teach them how to express intention and plan s by showing them the following sentences on the screen. (Slide show) I'm(not)going to... How are you going to...? I plan to... I'll... I'm looking forward to... Ask the students to look at the talking topics shown on the screen and discuss with their partners and then make up their own dialogues.(Show the following on the screen.) Talking Topics 1.Do you enjoy listening to poetry or reading it? Why or why not? 2.Do you enjoy writing it? Why or why not? 3.Is your experience of writing poetry like Wu Zhe's,Lily's or Chelsea's? Or is it different? How is it different? Give the stude nts three minutes to prepare and practice,and then ask two groups to demonstrate their dialogues in front of the whole class. Ste p 4 Homework Write a passage to introduce a kind of poem you like best. Step 5 Reflection after teaching _____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 教学参考 How to Write Poems About Feelings by Bruce Lansky Some of the best poems ever written are about feelings.You may want to write poems about your feelings,but perhaps you don't know how to begin. Here's a good way to get started: 1.On a piece of paper,write “sad” “mad” and “happy”.Now add as many feelings as you can to the list.If you're stumped for feelings,have a friend or two brainstorm with you.Sometimes two(or three)heads are better than one! 2.Choose one feeling from the list. 3.Write down your answers to one of the following questions: When do I feel [insert feeling]? Why do I feel [insert feeling]? How does it feel to be [insert feeling]? Your answer will become the poem,although you may want to revise and polish the poem as needed.What will make the poem work best is if it tells a story or if people can learn something about you from the poem.Often it's easier to write about feelings in free verse,which means you don't have to worry about rhythm and rhyme patterns.Just write whatever comes to mind. Here's an example: I feel miserable when... I have a big math test coming up so I have to study instead of watching my favorite TV show. My mother doesn't believe I have a fever,so I can't stay home and miss a big math test I didn't study for. My teacher doesn't believe I have a fever and refuses to send me to the school nurse until after the math test. I get a “D” on the math test. Here's another example that answers two questions:“When do I feel happy?” and “What is it like to feel happy?” When Santa brings me the toy I wanted most for Christmas I'm so happy I feel like: singing at the top of my lungs jumping in a mud puddle(too bad it's December and the puddle is covered with ice) raiding the cookie jar and eating all the cookies playing with my new toy all day and not letting my bratty little brother touch it for a single second(which,as I recall,is why my parents took away my favorite Christmas toy last year and hid it from me for one whole week) Finally,here's an example of a finished poem about what happens when you feel a little dazed and confused after a kiss: Scrambled I climbed up the door and I opened the stairs. I said my pajamas And buttoned my prayers. I turned off the covers And pulled up the light. I'm all scrambled up since She kissed me last night. Note:If writing poems about feelings brings up some confusing feelings or issues,talk to your parents or teacher.It may help to have a comforting,supportive person who can help you sort out what's on your mind. Period 5 Reading and Writing 整体设计 教学内容分析 The teaching materials of this period contain two parts.The first part is the reading passage on Page 14 with the title of I've Saved the Summer,which is a poem telling a parent speaking to a young adult child.The older person has experienced his/her own journey through life and is offering love to the young person to help him/her begin on his/her own journey through life.The second part is the Writing Task on Page 54,which asks the students to write a poem. 三维目标设计 Knowledge and skills 1.To enable the students to listen to the “music” of the poem,to know how it makes them feel and what it makes them think about. 2.To get the students to learn the following useful new words and phrases:appropriate,exchange,sponsor,darkness,try out,let out. 3.To get the students to learn the following useful structure: If I+past tense...,I would... 4.To help the students learn how to write a poem starting with “If I...”. 5.To foster the students' ability in skimming and looking up information in reference books and improve the students' reading ability. Process and methods Reading for specific information,summarizing,discussing and practicing. Emotion,attitude and value 1.To stimulate the students' love to poetry. 2.To inspire the students to write poems of their own. 教学重、难点 1.The understanding of the reading passage. 2.The use of the subjunctive mood in poem writing. 3.Teaching the students how to write a poem of their own. 教学过程 Step 1 Revision Check the answers to the grammar exercises on Page 13 and explain the difficult ones. Step 2 Pre-reading Listen to the poem “I've saved the summer” and answer these questions: 1.Do you think the speaker in the poem is more likely to be a girlfriend/boyfriend or a parent? 2.Does the poem have a rhythmic pattern? 3.Does the poem have rhyming words? 4.When you were listening to the poem,did it make you feel something or think about something? What did it make you feel or think about? Suggested answers: 1.Students' answers may vary. 2.Yes(it has two strong beats per line). 3.Yes. 4.Students' answers may vary. Step 3 Reading 1.Circle the words that rhyme.What is unusual about the rhyming words in the last four lines? 2.Try beating or clapping the strong beats of the rhythm as you read the poem to yourse lf.Now listen to the poem again and clap the strong beats. Suggested answers: 1.Circled words:you,new;need,feed;nineteen,mean;way,day;own,own.The rhyming words in the last four lines are unusual because they are the same word although they each have a different meaning. 2.The strong beats of the rhythm are marked below: I've saved the summer And I give it all to you To hold on winter mornings When the snow is new. I've saved some sunlight If you should ever need A place away from darkness Where your mind can feed. And for myself I've kept your smile When you were but nineteen Till you're older you'll not know What brave young smiles can mean. I know no answers To help you on your way The answers lie somewhere At the bottom of the day. But if you've a need for love I'll give you all I own It might hel p you down the road Till you've found your own. Step 4 Discussion In small groups discuss these questions: 1.Who is the speaker in the poem and who is he/she speaking to? Give reasons to support your answer. 2.Which of the following is the closest to the speaker's message? Give a reason for your choice. A.If it's cold,I'll warm you;if it's dark,I'll give you light;if you're hungry,I'll feed you;if you want love,I'll give it to you. B.Although the future may be difficult for you,whenever you need warmth and love,remember I'll have some to give you. C.While you're away I'll remember your smile and I'll love you always.When you return,I hope you will love me. Suggested answers: 1.A parent(mother or father)speaking to a young adult child(son or daughter). We know that the speaker is probably a parent because he/she is offering the child unconditional love(But if you've a need for love,I'll give you all I own).We know that the son/daughter is a young adult because the speaker refers to the time when you were but nineteen. 2.B Step 5 Language study Show the students the following language points in a slide show. 1.appropriate(P13) 【原句再现】 Match the beginning of each sentence with the appropriate ending. 把每个句子的开头与其合适的结尾连在一起。 【观察探究】 (1)Jeans are not appropriate for a formal party.牛仔裤不适合正式的晚会。 (2)Five million dollars has been appropriated for research into the disease. 拨款5 000 000美元用于研究这种疾病。 (3)He was accused of appropriating club funds. 他被指控挪用俱乐部的资金。 【归纳总结】 appropriate adj.恰当的,合适的;vt.拨(款等)做某种特殊用途;vt. 挪用,窃用 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)我认为这是一个提出我晋升问题合适的时刻了。 (2)政府已为建设医院拨出了一大笔钱。 (3)这个部长被发现挪用了政府用款。 Suggested answers: (1)I think this is an appropriate moment to raise the question of my promotion. (2)The government has a ppropriated a large sum of money for building hospitals. (3)The minister was found to have appropriated government money. 2.exchange,sponsor(P13) 【原句再现】 If there had not been an exchange program,he would not have found a sponsor to help him study abroad. 如果没有交流项目的话,他就不可能给自己找到一个出国学习的赞助人。 【观察探究1】 (1)We exchanged our opinions about the event at the meeting. 在会上,我们就此事交换了意见。 (2)He gave me an apple in exchange of an orange. 他给我一个苹果,交换一个橙子。 【归纳总结1】 exchange n. 交换,交换物,汇兑,交易所 v.交换,交易,兑换 【观察探究2】 (1)It is a pity that he doesn't have enough money to sponsor the project. 遗憾的是他没有足够的钱来支持这项计划。[来源:学,科,网] (2)My attempts to interest a sponsor missed fire several times,but I succeeded eventually. 我几次试图引起一个赞助人的兴趣,都没有达到目的,但最后还是成功了。 (3)Mr Robert Brown was announced as the sponsor. 罗勃特•布朗先生被宣布为赞助人。 (4)A wealthy sponsor came to our rescue with a generous donation. 有个富有的赞助人慷慨捐赠来解救我们。 【归纳总结2】 sponsor n.赞助者,发起者,主办者 vt. 发起,赞助,倡议 【即景活用】 根据汉语意思,用恰当的词填空。 (1)英镑与马克的兑换率是多少? What is the rate of ______between the pound and the mark? (2)她是我的入党介绍人。 She was my______ when I was applying for Party membership. Suggested answers:(1)exchange (2)sponsor 3.darkness(P14) 【原句再现】 I've saved some sunlight If you should ever need A place away from darkness Where your mind can feed. 我将所珍藏的阳光 全部都存留给你 让你在一个远离黑暗的地方 用温暖填满自己澄澈的心灵 【观察探究】 (1)The stars came out as soon as darkness fell.天一黑,星星就出来了。 (2)The whole jail was shrouded in darkness.整座监狱笼罩在黑暗之中。 (3)Darkness enfolded him.黑暗笼罩着他。 (4)The soldiers crept forward under the cover of darkness. 士兵在黑夜的掩护下向前爬行。 【归纳总结】 darkness n. 黑暗;黑夜 【知识链接】 dark adj. 黑暗的 n.黑暗,深色调,暗处 It's a dark and moonless night.这是一个黑暗无月的夜晚。 I'm getting married again,but keep it dark,will you?我要再婚了,可要保密呀,行吗? Some children are afraid of the dark.有些小孩怕黑。 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)A shadowy figure went past in the darkness. (2)The cat's eyes glowed in the darkness. (3)He turned off the light and the room was in complete darkness. Suggested answers: (1)一个模糊的身影从黑暗中闪过。 (2)猫的眼睛在黑暗中发亮。 (3)他关上了灯,室内一片漆黑。 4.try out(P15) 【原句再现】 I think I'll try_out his way too some time. 我认为将来的某个时候我也可以试一试他的方法。 【观察探究】 (1)She is raring to try out her new skates.她很想试试她那双新溜冰鞋。 (2)Please try out our red wine.请试试我们的红葡萄酒。 (3)Shirley will try out for the lead in the play.雪莉将参加该剧主角的选拔演出。 (4)His brother's example inspired him to try out for the football team. 他哥哥的榜样激励他去参加足球队的选拔测试。 【归纳总结】 try out vi. 试验;选拔(尤指运动比赛或者角色甄选) 【知识链接】 try on 指“试穿(衣服、鞋子)”及“试戴(帽子)”等,其中的on为副词,当宾语是代词时,该宾语要放在on之前;如果宾语是名词,该宾语放在on之前或之后均可。 try on a coat=try a coat on试穿大衣 The new hat is for you.Please try it on.这顶新帽子是给你的,请试试看。 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)他们正在试验那种新方法。 (2)那部收音机你应该试了再买。 Suggested answers: (1)They are trying out the new method. (2)You ought to try out that radio before you buy it. 5.let out(P16) 【原句再现】 Slowly the blackbird lets out a cry. 慢慢地,画眉鸟发出一声尖叫。 【观察探究】 (1)Each time she moved her leg,she let out a moan. 每次她动一下腿,就发出一声呻吟。 (2)When the land was seen,the sailor let out a whoop of joy. 当看见陆地时,那水手发出一声欢呼。 (3)He let out a volley of oaths. 他像发连珠炮似地破口大骂。 (4)The prisoners were let out to work in the garden. 囚犯们被放出到花园里去劳动。 (5)If the fuel is burnt,just heat is let out. 燃料如果被燃烧,就放出热。 (6)He opened the window to let out the foul air. 他打开窗户,放出污浊的空气。 【归纳总 结】 let out放出;泄露;放走 【即景活用】 翻译下列句子: (1)她把秘密泄露给了一个朋友。 (2)他们上星期被释放出狱。 Suggested answers: (1)She let out the secret to a friend. (2)They were let out of prison last week. 6.I intend to go for a hike in the countryside and sit quietly somewhere by myself. 我打算到乡村去作徒步旅行,自己静静地坐在某个地方。 intend to是表示“打算”的常用说法 ,类似的还有be going to,plan to,will,look forward to等。例如: I don't intend to chair the meeting.我不打算主持这次会议。 I intend to forgive him.我打算原谅他。 I'm not going to Dave's party tonight. 我今晚不打算去参加戴夫的晚会了。 Where do you plan to spend your holiday?你计划去哪里度假? I will do my best.我将会尽力而为。 I am familiar with his work and look forward to hearing his views on literary and artistic creation. 我熟悉他的作品,并期待他能就文艺创作问题发表自己的见解。 Step 6 Writing 1.Revise the grammar Work in groups.Write a list poem starting with “If I...” like Poem C.Write two lines each.It doesn't have to rhyme.Each group can choose one of these lines t o start their group poems.Then share these poems in class. Sentence patterns: (1)If I were the ruler of the world,I would... (2)If I had a million dollars,I would... (3)If I had taken your advice,I would have/wouldn't have... 2.Write a poem Ask students to write a poem that starts with “I feel happy when...”.The lines do not have to rhyme.Or write a poem that starts with “Slowly...”.Start each line with “Slowly” and make each pair of lines rhyme.To show the students what to do, list the first four lines of two sample poems.And ask students to write their own poems of eight to ten lines. Example A I feel happy when... The sky is blue, You smile at me with your sparkling black eyes, It's my birthday. Example B Slowly the moon climbs in the sky, Slowly the blackbird lets out a cry, Slowly the dog crosses the road, Slowly the old man carries his load. If time permits,the teacher asks students to finish their poems and share in class.If not,Tas k 2 of writing can be as homework. Step 7 Homework 1.Master the language points in the text. 2.Finish their poems after class. 3.Reread the poem “I've saved the summer” and appreciate the beauty of the poem. 4.Make more sentences with “If I had done...,I would...”. Step 8 Reflection after teaching ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 教学参考 How to Write a Cinquain Cinquain,despite its French-sounding name,is an American poetry form that can be traced back to Adelaide Crapsey.Crapsey,influenced by Japanese haiku,developed this poetic system and used it to express brief thoughts and statements.Other poets who popularized the form were Carl Sandburg and Louis Utermeyer.While the form does not have the extensive popularity of haiku,it is often taught in public schools to children because of the form's brief nature. Most cinquain poems consist of a single 22-syllable stanza,but they can be combined into longer works.A cinquain consists of five lines.The first line has two syllables,the second line has four syllables,the third line has six syllables and the fourth line has eight syllables,the final line has two syllables. The line length is the only firm rule,but there are other guidelines that people have tried to impose from time to time. Cinquain Guidelines Write in iambs(Two syllable groupings in which the first syllable is unstressed and the second syllable stressed.For example:I DRANK she SMILED we TALKED I THOUGHT)For the last line of the cinquain,however,both syllables should be stressed,NICE BAR. Write about a noun.Cinquains generally fail if you try to make them about emotions,philosophies or other complex subjects.They should be about some thing concrete. Don't try to make each line complete or express a single thought.Each line should flow into the next or the poem will sound static. Cinquains work best if you avoid adjectives and adverbs.This doesn't mean you can't have any,but focus on the nouns and the verbs.This almost always works best in a cinquain. The poem should build toward a climax.The last line should serve as some sort of conclusion to the earlier thoughts.Often,the conclusion has some sort of surpri se built into it. One possible,but not required,format is as follows: Line 1:title noun Line 2:description Line 3:action Line 4:feeling or effect Line 5:synonym of the initial noun. If you look at my examples,I prefer to use the noun as a separate title,not as part of the cinquain.Also,only one of the three poems is written in iambs. Sample cinquains: Tucson Rain The smell Everyone moves To the window to look Work stops and people start talking Rain came Opening Game Game time Season looked good National champions We told ourselves as we sat down Not now New Bar Across The street I went To drink at the new bar I drank she smiled we talked I thought Nice bar Period 6 Summing Up,Learning Tip and Assessment 整体设计 教学内容分析 This is the last teaching period of this unit,so the emphasis should be placed on going over and summarizing what has been learned in this unit.It includes the following parts:Summing Up,Learning Tip,Checking Yourself and some other consolidation exercises. Summing Up summarizes the whole unit from the aspects of topics,vocabulary and grammar.The teacher can first use this part to let students sum up what they have learned in this unit and then let them find out what they can't understand very well. Learning Tip gives students instructions on how to get the general idea of the text.Let the students think about what they already know about the topic and what new information they will find. Finally,ask students to finish Checking Yourself on Page 54 in the Workbook.This part aims at encouraging students to make a self-assessment after they finish learning this unit.It is very important to improve their learning.Of course,a testing assessment is also needed. In this period,the teacher can also provide more practice to consolidate what students have learned in this unit. 三维目标设计 Knowledge and skills 1.To get students to master all the useful new words and expressions in this unit. 2.To have students understand the new grammar item “Subjunctive Mood(2)” better,and enable them to use the following structure correctly:If I had done...I would have done... 3.To develop the students' ability to use the important language points in this unit. Process and methods Design some additional exercises for students to do in order that they can learn to use and grasp all the contents. Emotion,attitude and value 1.To encourage students to learn more about poetry and know more about some famous poets both at home and abroad. 2.To train the students to appreciate the beauty of poetry. 教学重、难点 Using what they have learned in this unit to solve real problems. 教学过程 Step 1 Revision 1.Check the homework exercises. 2.Dictate some useful new words and expressions in this unit. Step 2 Lead-in Ask the students to turn to Page 16.Think about what they have learned in this unit and tick the boxes to see how well and how much they have learned. Step 3 Summing up Five minutes for the students to summarize what they have learned in this unit by themselves.Then check and explain something where necessary. Suggested answers: (Students' answers may vary.)From this unit we have learned some simple forms of poems:nursery rhymes,list poems,cinquain,haiku and Tang poems.From the Workbook we have learned some other forms of poems,such as songs and adverb poems. From this unit we have also learned: useful verbs:tick,convey,tease,transform phrasal verbs:take it easy,run out of,be made up of,try out,let out useful nouns:exchange,sponsor,rhyme,nursery,diamond,pattern,cottage,sparrow,minimum,translation,branch,sorrow,librarian,section useful adjectives and adverbs:concrete,flexible,appropriate,eventually,contradictory,salty,endless,forever useful expressions:in particular,by chance/accident new grammar item:Subjunctive Mood(2) Step 4 Practice Show the exercises on the screen or give out exercise papers. Ⅰ.Word spelling 1.Can you r______ any poems you have read in high school,either in Chinese or in English? 2.I think you'd bett er consider other a______ of the matter. 3.Some poems try to c______ certain emotions. 4.The n______ teacher made the children sit bolt upright. 5.Mind your manners,guys! I want no r______ of your bad behavior. 6.The lady has a very expensive ring with a d______ in the centre. 7.Somebody dreamed of after retirement moving to a remote c______ in the countryside. 8.If you always t______ others like that,you'll miss the good opinion of your friends. 9.There is e______ work to do when you have children in the house. 10.He t______ the speech from Spanish into English. 11.Your room looks old.Why not t______ it by painting it? 12.He told me with s______ that his mother was very ill. 13.His casual clothes were not a______ for such a formal occasion. 14.If you are lost in the wood,it's very necessary to have a c______ with you. 15.The cloth has a p______ of flowers on it. 16.John was touched by the w______ of their welcome. 17.The truck was carrying a l______ of bananas. Ⅱ.Complete the passage using the words and expressions in the box in their correct forms. cottage,run out of,nursery,rhyme,minimum,convey,contradictory,pattern,translation,form When I was a baby,my mother used to read me ______ rhymes.I loved their ______ meaning and the way that the words ______ at the end of the lines.When I grew older,I was introduced to other ______ of poetry.Many of them also had a strong ______ which was repeated.The forms I liked best ______ their meaning by using the bare ______ ______ of words.Some of these forms came from Asia(like the haiku)and some of these were ______from their original language. When I______ new poems to read and enjoy,I would go to the library for some more.The librarian was a friend of my mother,and she would put poetry books on one side for me.In fact,my family love reading so much that we keep buying books.Now the living room of our ______ is full of books. Ⅲ.Translate the following expressions into Chinese. 1.make a list of ______ 2.expr ess feelings ______ 3.rhyming words ______ 4.an aspect of ______ 5.convey certain emotions ______ 6.nursery rhymes ______ 7.delight sb.______ 8.score goals ______ 9.take the eyes off the ball ______ 10.stay up ______ 11.take it easy ______ 12.run out of energy ______ 13.be made up of ______ 14.convey a strong picture ______ 15.be brimful of ______ 16.transform into ______ 17.translate into ______ 18.appropriate ending ______ 19.by chance ______ 20.pay attention to ______ Ⅳ.Multiple choice 1.—It is getting late.I am afraid I must be going now. —OK.______. A.Take it easy B.Go slowly C.Stay longer D.See you 2.What will the world use for power when it ______ oil? A.run out of B.is running out of C.has run out of D.ran out of 3.To enjoy the scenery,Irene would rather spend long hours on the train______ travel by air. A.as B.to C.than D.while 4.Don't believe him.He ______ a story. A.makes up B.is making up C.makes up of D.is making out 5.There are ______ these books and ______ pencils on the desk. A.a dozen;scores of B.scores;a dozen of C.scores of;a dozen D.two dozens;a score 6.He suggested that we ______ the plan later,which suggested that he ______ against it. A.discussed;was B.would discuss;should be C.discuss;was D.should discuss;should be 7.The train ______ over three hundred passengers over day. A.transmits B.ships C.conveys D.ferries 8.Look at the trouble I am in.If only I ______ your advice. A.followed B.would follow C.had followed D.should follow 9.Before leaving this country,you must be in ______ of a valid passport. A.provide B.possession C.own D.label 10.Everything ______ doing is worthy of ______ well. A.worthy;being done B.worthy;doing C.worth;being done D.worth;doing 11.The head office of the bank is in Beijing,but it has ______ all over the country. A.companies B.branches C.organizations D.businesses 12.They ______ two free tickets to Canada,otherwise they'd never have been able to afford to go. A.had got B.got C.have got D.get 13.He hears the little girl ______ a scream of terror when he was about to leave. A.set out B.let out C.come out D.give out 14.Nowadays young people,______ children,are ______ about their foods and clothes. A.especially;special B.especially;particular C.particularly;especial D.specially;especial 15.After having worked hard for so many years,Tom ______rose to the position of manager of the company. A.eventually B.unfortunately C.generally D.purposefully First get the students to do the exercises.Then the answers are given.The teacher can give them explanations where necessary. Suggested answers: Ⅰ.1.recite 2.aspects 3.convey 4.nursery 5.repetition 6.diamond 7.cottage 8.tease 9.endless 10.translated 11.transform 12.sorrow 13.appropriate 14.compass 15.pattern 16.warmth 17.load Ⅱ.nursery;contradictory;rhymed;forms;pattern;conveyed;minimum;translations;ran out of;cottage Ⅲ.1.把……列成一张表 2.表达思想 3.押韵的词 4.……的一方面 5.传达某种感情 6.童谣 7.使某人高兴 8.进球 9.没有留心看球 10.不睡觉,熬夜 11.放松,不着急 12.精疲力竭 13.由……组成 14.呈现一幅清晰的画 15.洋溢着…… 16.改变,转变成…… 17.翻译成…… 18.恰当的结尾 19.碰巧 20.注意到,留意到 Ⅳ.1~5 DCCBC 6~10 CCCBC 11~15 BBBBA Step 5 Learning tip Ask the students to turn to Page 16.Read through the passage and make sure they understand it.Encourage them to do as the passage tells because if they are doing so they will be teaching themselves a useful way of learning. Step 6 Assessment 1.Checking yourself(on Page 54 in the Workbook) First get the students to think about the 6 questions individually.Then they can discuss in groups sharing their experience.The teacher can join in and give them advice and suggestions where necessary. 2.Testing assessm ent (1)Complete the following dialogue with the proper forms of the verbs given. Tom:What ______ you ______(do)at this moment if you were at home? Henry:Playin g cards,maybe. Tom:If I had known you liked cards,I ______(buy)some yesterday.If I happen to see them tomorrow,I______(buy)them. Henry:Oh,if I liked them so much,I______(bring)some with me yesterday.I______(not mind)at all if I didn't play here.We ______ only ______(waste)this nice weather if we were playing cards now.It______(be)much nicer if we could go walking. Tom:Why not? (2)Study the example below together with your group members.Then complete the following sentences with the proper forms. Example:If I_hadn't_taken your advice,I would_have_made a bad mistake. ①If I had a cold,_________________________________________________________. ②If you were in his place,_________________________________________________. ③It would be nice _________________________ __________________________. ④If I had left a little earlier,___________________________________________________. ⑤She would have come _______________________________________________________. (3)Match the two parts of the sentences. ①If I knew why she ran away, a.if you met a monster? ②She would sleep better, b.if you thought I was behaving badly? ③If I saw his face again, c.I would know it immediately. ④Would you tell me, d.I would tell you. ⑤If cloning were banned, e.if she watched fewer hor ror films on TV. ⑥Wouldn't it be terrifying, f.this research would end tomorrow. Suggested answers: (1)would;be doing;would have bought;shall buy;would have brought;wouldn't mind;would;be wasting;would be (2)①I would stay in bed ②you wouldn't do it in that way ③if we went together ④I could have arrived on time ⑤if she hadn't had another appointment (3)①d ②e ③c ④b ⑤f ⑥a Step 7 Homework 1.Finish off the Workbook exercises. 2.Review and summarize what you have learned in Unit 2. Step 8 R eflection after teaching 教学参考 诗歌欣赏(课外欣赏) 1.If I Could Catch a Rainbow 如果我能留住彩虹 If I could catch a rainbow 如果我能留住彩虹 I would do it just for you 我将只为你一个人挽留[来源:学*科*网] And share with you its beauty 在你感到忧伤的日子[来源:Z*xx*k.Com] On the days you're feeling blue. 与你分享它的美丽 If I could build a mountain 如果我能建造大山 You could call your very own 你尽可把它当成你自己的 A place to find serenity 体验宁静的空间 A place to be alone. 独处的地方 If I could take your troubles 如果我能带走你的烦恼 I would toss them into the sea 我会把它们通通扔进大海 But all these things I'm finding 然而我发现所有这些事情 Are impossible for me. 我都无能为力 I cannot build a mountain 我建不成一座大山 Or catch a rainbow fair 也留不住彩虹的美丽 But let me be what I know best 就让我做你最好的朋友吧 A friend that's always there. 永远与你相伴 2.月下独酌 Drinking Alone Under the Moon 李白 Li Bai 花间一壶酒 Among the flowers from a pot of wine 独酌无相亲 I drink alone beneath the bright moonshine. 举杯邀明月 I raise my cup to invite the moon,who blends 对影成三人 Her light with my shadow and we're three friends. 月既不解饮 The moon does not know how to drink her share; 影徒随我身 In vain my shadow follows me here and there. 暂伴月将影 Together with them for the time I stay 行乐须及春 And make merry before spring's spend away. 我歌月徘徊 I sing the moon to linger with my song; 我舞影零乱 My shadow disperses as I dance along. 醒时同交欢 Sober,we three remain cheerful and gay 醉后各分散 Drunken,we part and each goes his way. 永结无情游 Our friendship will outshine all earthly love; 相期邈云汉 Next time we'll meet beyond the stars above. 3.Why am I the one that has to die? I went to a party,Mom,I remembered what you said. You told me not to drink,Mom,so I drank soda instead. I really felt proud inside,Mom,the way you said I would. I didn't drink and drive,Mom,even though the others said I should. I know I did the right thing,Mom,I know you are always right. Now the party is finally ending,Mom,as everyone is driving out of sight. I started to drive away,Mom,but as I pulled out into the road, the other car didn't see me,Mom,and hit me like a load. As I lay there on the pavement,Mom,I hear the policeman say, the other guy is drunk,Mom,and now I'm the one who will pay. I'm lying here dying,Mom...I wish you'd get here soon. How could this happen to me,Mom? My life just burst like a balloon. There is blood all around me,Mom,and most of it is mine. I hear the doctor say,Mom,I'll die in a short time. I just wanted to tell you,Mom,I'm certain that I didn't drink. It was the others,Mom.The others didn't think. He was probably at the same party as I. The only difference is,he drank and I will die. Why do people drink,Mom? It can ruin your whole life. I'm feeling sharp pains now.Pains just like a knife. The guy who hit me is walking,Mom,and I don't think it's fair. I'm lying here dying and all he can do is to stare. Tell my brother not to cry,Mom.Tell Daddy to be brave. And when I go to heaven,Mom,put “Daddy's Girl” on my grave. Someone should have told him,Mom,not to drink and drive. If only they had told him,Mom,I would still be alive. My breath is getting shorter,Mom.I'm becoming very afrai d. Please don't cry for me,Mom.When I needed you,you were always there. I have one last question,Mom,before I say good bye, I didn't drink and drive,so why am I the one that has to die?查看更多