- 2021-05-22 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 56页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
2018届二轮复习动词时态和语态课件(56张)
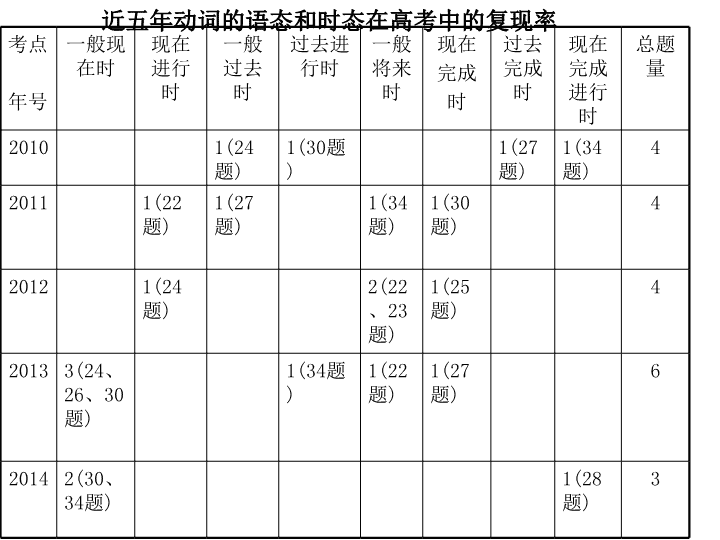
2018 届二轮复习 动词的时态和语态 时态和语态的主要考点 1 、考查在语境中判断动词时态的运用能力。常考的时 态为:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、现在进 行、过去进行、现在完成、过去完成、现在完成进 行、过去将来等。 2 、时间、条件、让步等状语从句中动词的时态;主从 句时态呼应问题。 3 、持续性动词和终止性动词的用法区别。 4 、及物动词的被动语态。 5 、系动词的用法特点。 6 、某些以主动形式表被动意义的动词的用法。 近五年动词的语态和时态在高考中的复现率 考点 年号 一般现在时 现在进行时 一般过去时 过去进行时 一般将来时 现在 完成 时 过去完成时 现在完成进行时 总题量 2010 1(24 题 ) 1(30 题 ) 1(27 题 ) 1(34 题 ) 4 2011 1(22 题 ) 1(27 题 ) 1(34 题 ) 1(30 题 ) 4 2012 1(24 题 ) 2(22 、 23 题 ) 1(25 题 ) 4 2013 3(24 、 26 、 30 题 ) 1(34 题 ) 1(22 题 ) 1(27 题 ) 6 2014 2(30 、 34 题 ) 1(28 题 ) 3 常考时态 一般现在时 现在完成时 一般将来时 一般过去时 现在进行时 过去进行时 现在完成进行时 过去完成时 现在完成时 过去进行时 考查比例较大的几点 状语从句的动词时态 一般将来时 最常用的几种时态与时间状语的搭配 一般现在时 现在进行时 现在完成时 现在完成进行时 often, always, usually, sometimes, on Sunday, every …, at weekends, once in a while, three times a day… (right) now, at this moment, at present, for the time being, this year, always, … for, since, so far, in/over/during the past/ last few years, lately, recently, just, up to now, up till now, already, yet, ever, never, twice, three times, before, … all the time, all this morning, for, since, in the past few years, … 最常用的几种时态与时间状语的搭配 一般过去时 过去进行时 过去完成时 过去将来时 yesterday, last…, the day before yesterday, …ago, in 2000, in the past, the other day, just now, once upon a time,… at 10 last night, then, this morning, at that time/ moment, this time yesterday, last year, always, … by+ 过去时间, by then, by the end of + 过去时间, by the time you did sth,….. 最常用的几种时态与时间状语的搭配 一般将来时 将来进行时 将来完成时 tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, in 2020, in a few years, in future, in the future, soon, next…, another day, … at 10 tomorrow, then, this time tomorrow, next year, … by + 将来时间 , by then, by the end of + 将来时间 , by the time you do sth, … 考题点击 1 、 2 1. Months ago we sailed ten thousand miles across this open sea, which ___ the Pacific, and we met no storms. A . was called B . is called C . had been called D . has been called 2. I _____ ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the new year. A. will play B. have played C. played D. play B 本题的干扰源为上下文的过去时,但“被称为太平洋”是客观事实,只能用一般现在时。 常识告诉我们,一个人一旦获得某种技能,一般是不会在短期内失去的,所以需用一般现在时。 D 一般现在时 一般现在时表示: 1. 经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态。 2. 主语现在的特征、性格和状态。 3. 客观真理。 He seldom asks me for advice. There are regular flights between the two cities. China is a developing country which belongs to the third world. All the living things on the earth depend on the sun. 考题点击 3 I don’t know when he ____, but when he ____, I will let you know. A. will come, will come B. comes, comes C. will come, comes D. comes, will come C 第一个 when 引导宾语从句,从句表将来用一般将来时态。第二个 when 引导时间状语从句,只能 用一般现在时态表将来 。还有条件、让步状语从句也如此。这时,主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时, “主将从现”。 If you __________( 不去 ) there tomorrow, _______________ ( 我也不去 ). _______________________________( 无论你给他多少建议 ), he will do exactly what he wants. Take an umbrella ______________( 以防下雨 ). neither/nor will I However much advice you give him in case it rains don’t go The next train _________(leave) at 3 o’clock this afternoon. The film _________(start) at seven o’clock and _________(end) at nine o’clock this evening. The plane _________(take) off at 8:00a.m.. It is 7:10a.m. now. We must hurry up. leaves starts ends takes 4. 一般现在时表示按安排或计划要做的动作( 有具体的时间状语 )。限于 come, go, leave, begin, start, end, open, close, return, arrive, take off, stop, depart 等。 The film, ____________(start) at seven o’clock, attracted many young people. starting Translation: 公共汽车来了。 铃响了。 Here comes the bus. There goes the bell. 用于倒装句,表示动作正在进行。 = The bus is coming. = The bell is ringing. Make sure that all the windows ____________ (close) before you leave the room. are closed make sure (that) 后面的宾语从句中用一般现在时态。 写作句型:随着 … 而来的是 … 倒装句 Along with…, there come(s) … Along with the physical changes, there come some psychological changes. 考题点击 4 、 5 4. Since I won the big prize, my telephone hasn't stopped ringing. People _____ to ask how I am going to spend the money. A. phone B. will phone C. were phoning D. are phoning 5. Selecting a mobile phone for personal use is no easy task because technology _____ so rapidly. A. is changing B. has changed C. will have changed D. will change D 自从我赢了大奖,人们不停地打电话来问我将怎样使用这笔钱。此处的 are phoning 表示“在不停的打电话”。 A 选择移动电话难的原因是由于科技 正在 飞速发展,表日新月异的变化,所以要用现在进行时。 现在进行时的用法: Look ! It is raining cats and dogs now. 表现在正在进行(说话的瞬间)的动作。 2. 表当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作(说话时不一定正在进行)。 3. 表示说话人对主语的行为表示赞叹或厌恶,常与 always, constantly 等连用。 4. 表示按计划或安排在最近要进行的事情。 go, come, leave, start, arrive, return, sleep, stay, do, leave, wear, work 等表移动、方向的动词。 I am writing a novel these days. The children are always making trouble. His money is running out. ◆ We must look around when _________(cross) the road. Take care while ________(ride) a bicycle. crossing riding when we are crossing the road while you are riding a bicycle 省略句:时间、条件、让步状语从句中如果是现在进行时态,引导词后可省略主语和 be 动词,直接用 v-ing 的形式。 ◆ _____________________________________( 参加会议的有 700 学生 ) from Peking University. ______________________________( 一幅画挂在墙上 ) by Qi Baishi. Attending the meeting are 700 students Hanging on the wall is a painting 倒装句:现在进行时态的句子,可以把 doing 表语提到句首,用全部倒装。 Doing+ be+ 主语。 考题点击 6 、 7 6._____ my sister three times today but her line was always busy. A. I’d phoned B. I’ve been phoning C. I’ve phoned D. I was phoning 7. Though we don’t know what was discussed, but we can feel the topic _____. A. had changed B. will change C. was changed D. has been changed C D 此题的干扰源是后面的 was busy 。今天打了三次电话是用来表示结果的,只能用现在完成时;而每次她都占线是表示过去的动作,所以用一般过去时。 尽管不知道讨论过什么,但感觉到话题已经改换了,表示结果。 现在完成时态的用法: I have seen the film already. I have had lunch. I am not hungry. He has lived here since 10 years ago. He has been to London three times. 1. 到现在为止已经完成的动作。 3. 过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态,常和表示 包括现在 在内的一段时间的状语连用。 2. 过去发生或已完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响。 4. 表反复或习惯性的动作,常与 …times 连用。 ◆ ---- _____ you ______ (have) lunch yet? ----- Yes. I _______(have) lunch at home. Have had had 到现在为止是否已经吃饭了,强调结果,用现在完成时。回答时表具体在哪里吃的,表过去的动作,用一般过去时。 ◆ It is the most instructive lecture that I ________________ (ever, attend) . have ever attended 在“最高级 + 名词” 之后跟定语从句,从句用现在完成时。 ◆ This is the first time that I _____________ (visit) your country. have visited It / This is the first/second/ last… time that 从句中用现在完成时。 It / This was the first/second/last…time that 从句中用过去完成时。 ◆That man can’t be Green; he _____ to the USA. A. went B. has gone C. has been to D. had gone B went 只表过去曾经去过某地,和现在没关系。 has gone to 表去 … 了 ( 或到了或在途中 ) , has been to 去过 …( 已回来 ) ◆ We will set off at once if the rain ____________ (stop). You’d better not give up this job until you ___________ (find) a better one. has stopped have found 用于时间、条件状语从句中,表示从句动作先于主句动作之前完成 ◆ The book, which became the best-seller, was written by Arthur’s wife, Joan, whom he ___________________ (marry) for 52 years. has been married to marry 是终止性动词,不可与延续性状语 for, since 等连用,需把终止性动词变成可延续的动词形式 be married to 。其它词有: die--- come--- leave-- begin— join--- become— borrow--- buy--- get in touch with--- fall in love with--- be dead be here be away (from) be on be in be keep have be in touch with be in love with 考题点击 8 、 9 8.--- Hi, Tracy, you look tired. --- I am tired. I _____ the living room all day. A. painted B. had painted C. have been painting D. have painted 9. Now that she is out of a job, Lucy______ going back to school, but she hasn’t decided yet. A had considered B has been considering C considered D is going to consider 她“一直在考虑返校”是现在完成进行时,“还没作决定”是现在的结果。 C B 这句话的意思是“我一整天都在刷起居室”,现在完成进行时表示从过去开始的一个动作一直持续到现在,而且还在进行当中。强调的是“一直在做”。 现在完成进行时的用法: She is very tired. She has been typing letters all day. All these years they have been contributing articles to our magazine. 1. 表示从过去某一时刻开始的动作一直延续到现在,甚至会延续到将来(强调延续)。 2. 到现在为止的一段时间里一再反复发生的动作。 高考题点击 10 、 11 、 12 : 10. --- Nancy is not coming tonight. --- But she _____! A. promises B. promised C. will promise D. had promised 11. My uncle _____ until he was forty-five. A. married B. didn’t marry C. was not marrying D. would marry Nancy 答应要来这个动作应该发生在过去,是过去作出的承诺。 until 用在肯定句中时,主句的动词必须是延续性动词,表示该动作一直持续到 until 后的时间为止;短暂性动词只能用在否定句中,表示直到此时该动作才开始。本题中 marry 是短暂性动词,所以只能用在否定句中。 B B 12. --- You haven’t said a word about my new coat, Brenda. Do you like it? --- I’m sorry I _______ anything about it sooner. I certainly think it’s pretty on you. A. wasn’t saying B. don’t say C. won’t say D. didn’t say 本题的干扰源来自上下文中的时态,上文用的是现在完成时,下文用的是一般现在时,所以有些人就误以为此处该用现在时态了。但根据说话人的意思不难发现,没有说出自己的评价是 在这段对话以前的事 了,所以要用一般过去时。 D 一般过去时的用法: The Great Wall came into being in 221 BC. When in Shanghai, I often went to school by bus. He put a finger in his mouth, tasted it and smiled with satisfaction. He said he would call us as soon as he arrived home. 1. 表过去发生的动作或存在的状态。常与表过去的时间状语连用。 2. 表过去一段时间里经常或反复发生的行为。 used to do 和 would do 也表这意思。 3. 表过去先后发生的一连串的动作。前若干动作后用逗号隔开,最后两个之间用 and 连接。 4. 在时间、条件状语从句中,用一般过去时表示过去将要发生的动作。 比较 He will come to the party if he ________ (be) free. He said he ___________(come) to the party if he ________(be) free. is would come was is, was 表示现在和过去将要发生的动作。 时态呼应原则:当主句谓语动词为一般过去时态,宾语从句只能用相应的过去时态(一过、过进、过完、过将),除非是客观真理,总用一般现在时。 I didn’t know where _____ my purse. A. have I put B. had I put C. I have put D. I had put D 根据时态呼应原则排除 A,C, 根据陈述句语序选 D ◆ When Alice came to, she did not know how long she ______ there. A. had been lying B. has been lying C. was lying D. has lain ◆The moment I got home, I found I ____ my wallet on the playground. A. had left B. has left C. have left D. was leaving A A 根据时态呼应原则排除 B,C, 根据时间先后选 A 根据时态呼应原则排除 B,D, 根据时间的先后选 A ◆ Edward, you play so well. But I _____ you played the piano. A. didn’t know B. hadn’t known C. don’t know D. haven’t known A C,D 与现在有关,表示现在不知道。根据句意,指过去不知道,现在已知道。 B 表过去的过去,这里只表现在的过去。 ◆--- Alan is ill in hospital. ---- Oh, really? I _____________ (not, know). I __________(go) and visit her. ◆What a nice house! I _______________(never, think) that one day I ________________( live) in such a beautiful house. ◆---Alice, here is your car key, in the drawer. ---- Thank you. I _______________(not, realize) that I _____________(leave) it here. didn’t know will go never thought would live didn’t realize had left Alice _____ in America for 10 years, but she never regrets she has come back to China. A. has worked B. worked C. had worked D. has been working B It is said in the book that Thomas Edison (1847-1931)____ the world leading inventor for 60 years. A. would be B. had been C. has been D. was 易错题 D 误选 A ,但现在完成时是包括现在的时间在内的。这里表已经回来了,在美国工作成为了过去,用一般过去时。 for 60 years 未必只能和现在完成时连用。这里是讲述过去一段时间的经历,用一般过去时。 It is time you ____________________( 承担责任 ). It is time you _____________________( 进行休学实践年 ). took on the responsibility took the gap year It is time (that) sb. did sth. 虚拟语气: “该做某事的时候了”。 _______________ ( 如果我是你的话 ), I would distribute the money to the poor. ________________( 如果我有一百万 ), I would travel to every point of the compass. If I were you If I had a million dollars If 虚拟条件句中,与现在事实相反的假设,用一般过去时表示。 It was not long before they _________(occupy) the city center It was not long since they __________ (occupy) the city center. occupied 不久之后就 … had occupied 自从 … 有多久了 考题点击 13 13. The manager had fallen asleep where he _____, without undressing. A. was laying B. was lying C. had laid D. had lied B 该题的意思为“经理躺在那儿睡着了,衣服也没脱”。 “躺”是一个不及物动词,其过去式和过去分词为“ lay; lain” 。 lay 是及物动词,过去式和过去分词为 laid ; lied 是“说谎”的过去式和过去分词。 过去进行时的用法: The first time I saw her , she was standing in his study. He was writing a novel last year, but I don’t know if he has finished it. He was constantly leaving things here and there at that time. He said he was coming to see you the next month. 1. 过去每一时刻正在进行的动作,除有上下文暗示外,一般和时间状语连用。 2. 过去某一时间段正在进行的动作。 3. 与 always 或 constantly 连用,表示说话人过去对主语的行为表赞叹或厌恶等。 4. 表过去将要发生的动作,一般限于表移动,方向的动词。 I was wondering if I could ask you a question? My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself. 5. 某些表心理活动的词,用于过去进行时, 表示委婉、客气,而不表过去。 6. 描述一件事情发生的背景。 考题点击 14 14. As she ____the newspaper, Granny ____asleep. A. read, was falling B. was reading, fell C. was reading, was falling D. read , fell 一般来说在复合句中的两个动作, 延续性的动作 (长动作)大都用过去进行时, 短暂性的动作 (短动作)用一般过去时,表示在某个动作进行的过程当中另一个动作发生了。 B ◆ They ____________(have) a meeting when the fire ________(break) out. ◆ Jane ___________(meet) Frank while she ______________(live) in Holleywood. ◆ The UFO __________(travel) from east to west when I _________(see) it. were having broke met was living was travelling saw ---- Please repeat what I said just now. ---- Sorry, I _____. A. didn’t listen B. wasn’t listening C. hadn’t listened D. won’t listen B when you said it. ---- We could have got in for nothing. ---- Yes, nobody ____ tickets. A. collected B. has collected C. was collecting D. had collected C when we got in. 在隐含过去进行时,表示“当时正在做某事”时,可以在后面加上 when 从句理解。 比较: He __________ (write) a novel last year. He __________a novel last year, but I don’t know whether he has finished it. wrote was writing 当时正在写 写完了 写作:描述背景 这是一个寒冷的冬天。北风猛烈的刮,厚厚的雪落下来。一个可怜的小女孩在街上走,这时 … It was a cold winter. The north wind was blowing hard and heavy snow was falling. A poor girl was walking in the street when… …was /were doing sth. when …did sth…. 句型: … 正在做某事,这时 … 考题点击 15 、 16 15. The little girl ____ her heart out because she ____ her toy bear and believed she wasn’t ever going to find it. A. had cried, lost B. cried, had lost C. has cried, has lost D. cries, has lost 16. — Hurry up! Alice and Sue are waiting for you at the school gate. — Oh! I thought they _____ without me. A. went B. are going C. have gone D. had gone B D 根据时态呼应原则排除 B , C 。“他没叫我就走了”这个动作明显发生在“我认为”之前。所以必须用过去完成时。 哭得伤心发生在过去,而丢玩具熊发生在哭之前。两个发生在过去的动作,之前发生的用过去完成时,之后发生的用一般过去时。 过去完成时的用法: He had worked there for 10 years before he reached Canada. By the end of last year, the power plant had been completed. He told me he had made much progress . We had hoped to catch the 9:30 train, but we failed to. 1. 表在过去某一时间或动作之前已完成的动作或存在的状态,表“过去的过去”。这个时间可用短语或从句表示,也可上下文加以衬托。 2. 用在主句是过去时的间接引语和宾语从句中,表 示已经完成的动作。 3. 表过去本打算实现而未实现的希望或计划。常用的动词有 hope, want, expect, think, mean, suppose, plan, intend 等 If you ___________(win) the first place in the last exam, you _____________(get) the iPad as a gift from your father. But you didn’t . had won would have got 虚拟语气中与过去事实相反的假设, if 从句用过去完成时。 How I wish I _____________(take) your advice last time. If only you ____________(donate) more money yesterday. I’d rather you ___________(tell) him the truth when you saw him last time. had taken had donated had told Wish, if only, would rather 后的宾语从句中的虚拟语气用过去完成时表与过去事实相反的假设。 考题点击 17 、 18 Twenty years ago nobody could predict he _____ such a famous scientist. A. became B. will become C. have become D. would become The discovery of gold in Australia led thousands to believe that a fortune ____. A. is made B. would make C. was to be made D. had made D C 20 年前预测未来,表过去的将来,用过去将来时。 过去的一个发现使得人们相信将来可以发财,是过去将来。 过去将来时的用法: He told me that he would take an important exam the next week. The time was not far off when he would regret this decision. 表示在过去的某一时刻看来将要发生的事,常常用于主句谓语为一般过去时的宾语从句中。 过去将来时的其它表示: Last Friday we decided we were going to the Great Wall. It was reported that another bridge was to be built across the Yangtze River. He didn’t know when you were coming. He was about to dive when he saw a shark. She was on the point of leaving when I arrived. was / were going to do sth. 打算 was / were to do sth 打算、计划 was / were doing sth. 将要 was / were about to do sth. 就要、正要 was / were on the point of doing sth. 正要 句型: … 正在做某事,这时 … … 正要去做某事,这时 … … 就要去做某事,这时 .. was / were doing sth. when …did sth. was / were about to do sth. when …did sth. Was / were on the point of doing sth. when … did sth. 考题点击 19 、 20 : If a man _____ succeed, he must work as hard as he can. A. will B. is to C. is going to D. should 20. --- You’ve left the light on. --- Oh, so I have. _____ and turn it off. A. I’ll go B. I’ve gone C. I go D. I’m going B A 此句的意思为“如果一个人想要成功,就必须尽力而为”。 If 引导的是条件状语从句,不能用将来时。而 be to 结构虽然表示将来的动作,但它不属于将来时。 Will do 表临时做出的决定。 一般将来时的表示: When I retire, I shall have more time for painting. The play is going to be put on next month. He and I are to meet at the theatre. He is about to start on a journey. How are you going, by boat or by train? I’ll let him know if he comes here. will / shall do sth. 将要 be going to do sth. 打算、将要 be to do sth. 打算、计划 be about to do sth. 就要做 … be doing 将要 一般现在时表将来 ---Look! The lights in the room are still on. You must have forgotten to turn them off. --- Sorry, I _____ to turn them off now. A. will go B. am going C. am to go D. have gone A will do 通常指纯粹的将来或事先未计划好的,临时性的决定。 be going to 表事先有计划的意图,是经过考虑的。侧重于说话者个人意图或打算。也表某种客观迹象预示即将会发生。 be to 表按计划、安排将要发生的动作,侧重于受别人的指示或安排。表由于客观因素或不受人的控制将要发生的动作,只用 be going to ,不用 be to It is going to rain. Am I to finish the work on my own? I am going to try my best to help her. 客观迹象 别人安排 个人意图 be to do sth. 的几种用法: A tall building is to be built in this area. (按计划安排)打算、将要做 Nobody is to leave the room without my permission. ( 按命令、指示、约定、要求等 ) 必须,必要,应该做 Troubles never come singly. The worst is still to come. 表后来命运注定会发生 If you are to pass the exam, you will have to study harder from now on. ( 用于条件句 ) 想,想要做 Stand higher, and you ________(see) farther. Study hard, or you ________ (fall) behind others. will see will fall 祈使句 + and / or + 一般将来时 …, 就会 / 否则 … It _______(be) long before he shows up again. will be It will be … before sb. does sth. 多久之后才 / 就 … 考题点击 21 If you plant watermelon seeds in the spring, you ____ fresh watermelon in the fall. A. eat B. would eat C. have eaten D. will be eating D 在春天种下西瓜子,将在秋天收获新鲜的西瓜。相当于 will eat Will be doing 在单纯表示未来动作时可以代替 will do, 但是如表示说话者主观意图, 邀请或允诺时,通常用 will do Will you be having dinner at home this evening? Will you have dinner at home this evening? Will you have dinner with me this evening? 邀请 考题点击 22 By the time Jane gets home, her aunt ____for London to attend a meeting. A. will leave B. leaves C. will have left D. left C 将来完成时的用法: 到将来某个时间为止将已经完成的动作或存在的状态。 By next month, we ______________(save) enough for a used car. By 10 a.m. tomorrow, I ___________________ (finish) the speech and _______________(have) a chat with the students then. will have saved will have finished will be having 被动语态的表示: 一般时态: 进行时态: 将来时态: 完成时态: 宁愿被: 最好被: 打算被: 过去常常被 情态动词 is / am / are /was /were done is/ am / are/ was/ were being done will/ would be done have / has/ had been done would rather be done had better be done be going to be done; be to be done used to be done 情态动词 + be done The book ______ (sell) well. By today 50,000 copies _______________(sell) out. sells have been sold sell well 强调主语的 特性 ,主动表被动。第二个 sell 强调被卖掉的 动作 。 主动表被动 1. 某些“不及物动词 + 副词 (easily, well, smoothly, quickly, badly 等 )” , 说明主语的特性。动词有 lock, open, close, sell, bend, print, cut, wash, read, write, wear, tear, cook 等。 易撕 书写流畅 易洗 好读 熟得快 打印质量差 易弯曲 tear easily wash easily cook quickly bend easily write smoothly read smoothly print badly I want to taste the food _______(smell) delicious. The method _________________(already, prove) practical. smelling has already proved 2. 系动词 look, sound, taste, smell, feel, prove, remain, seem 等无被动语态,作定语,用 doing The novel is interesting __________(read). We find the box heavy __________(carry). to read to carry 3. Sth. is +adj. + to do . I find/ think/ make/ feel sth. + adj. + to do . to do 是主动表被动 The car ___________ ( 开不动了 ). The door of the classroom ___________ ( 锁不上 ). won’t move wouldn’t lock 4. 某些与 won’t, wouldn’t 连用的不及物动词如 lock, open, close, move, print, shut 等, 用主动表被动。 I have a letter _________(type), so I can’t go with you. With a lot of problems _________ (solve), I am at a loss now. to type to solve 5. have sth. to do; There is sth. to do.; with sth. to do. 有 … 要做 比较: He asked me if I had anything ___________ (type). to be typed type 的逻辑主语不是 I ,用 have sth. to be done It is I that ___________ (blame) for the incident. am to blame 6. sb. is to blame (for sth.). 该怪 … , … 该负责任 The question is well worth _________ (discuss). The naughty boy deserves __________(criticize). discussing 7. sth. is (well) worth doing. 很值得 ( 被 )… deserve doing … 值得被 … , … 应该受到 … The computer needs ____________(repair). repairing 8. sth. needs / wants / requires doing. 需要被 … criticizing The car is too old __________(drive). to drive 9. Sth. is too… to do . 太 … 而不能 … Sth. is …enough to do. 足够 … 去 …查看更多